Figure 6.
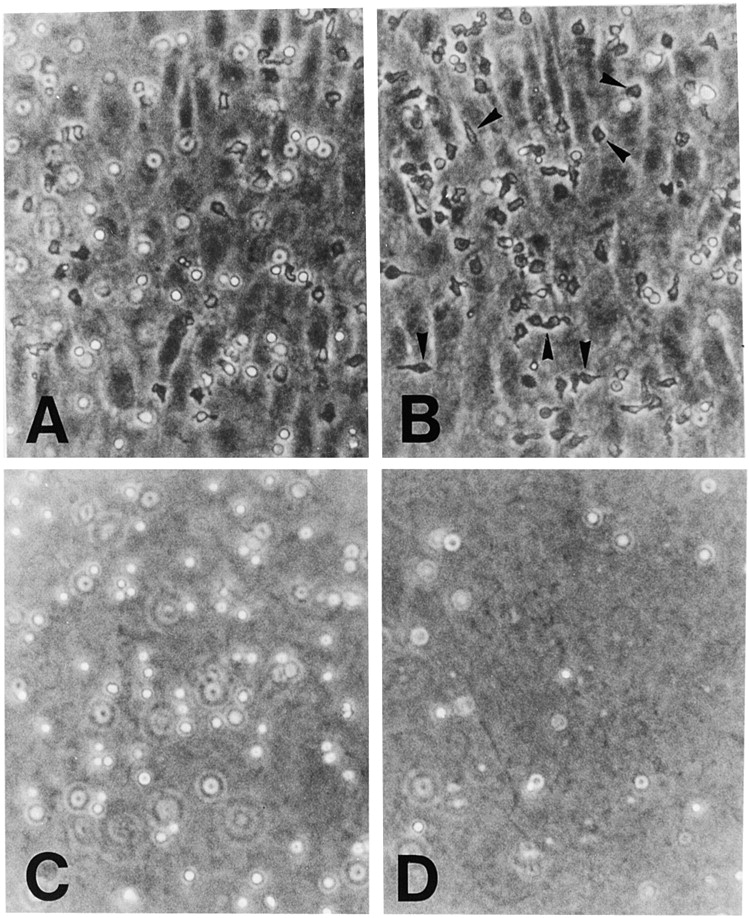
Anti-4C8 mAb inhibits T cell transmigration at the intercellular junctions of HUVECs. T cells were incubated on IFN-γ–stimulated (500 U/ml, 48 h) HUVEC monolayers cultured on collagen gels in the presence of anti-4C8 (1 μg/ml; B and D) or control IgG3 (1 μg/ml; A and C). After 4 h, monolayers were washed to remove nonadherent cells and fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde in PBS or further treated with 0.4% EDTA to remove monolayers from the surface of collagen gels. Cells were photographed under a phase–contrast microscope (×100). In the control Ab sample, although a number of T cells still adhered to the apical surface of the HUVEC monolayer (A), numerous cells that migrated into the collagen gel below could be seen (C). However, in the anti-4C8– treated sample, migration was strongly inhibited (D), whereas the number of adherent cells was increased (B) compared to the control. Most adherent cells appear to be arrested at the EC junctions (B). The black arrows indicate these T cells.
