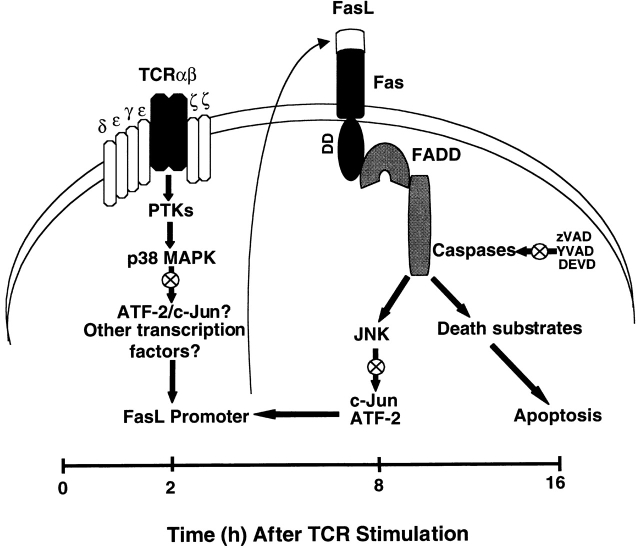
Figure 8.
Model of regulation of FasL expression during TCR-induced T cell AICD. In this model, TCR ligation leads to the activation of PTKs, which results in the activation of p38 MAPK. p38 MAPK then phosphorylates several nuclear transcription factors (e.g., ATF-2), which may bind to the FasL promoter and activate FasL gene transcription. Transcribed FasL protein translocates from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane, interacts with Fas which then recruits FADD to bind to its death domain. This FasL–Fas interaction initiates a caspase cascade that subsequently activates JNK. Activated JNK promotes AICD by regulating FasL expression. Thus, p38 MAPK and JNK may preferentially regulate FasL expression at early and later times after activation, respectively, perhaps by the phosphorylation and activation of distinct transcription factors for the FasL promoter. Consistent with this model, we observed that inhibition (⊗) of p38 MAPK, JNK, and caspase activity blocks T cell AICD.