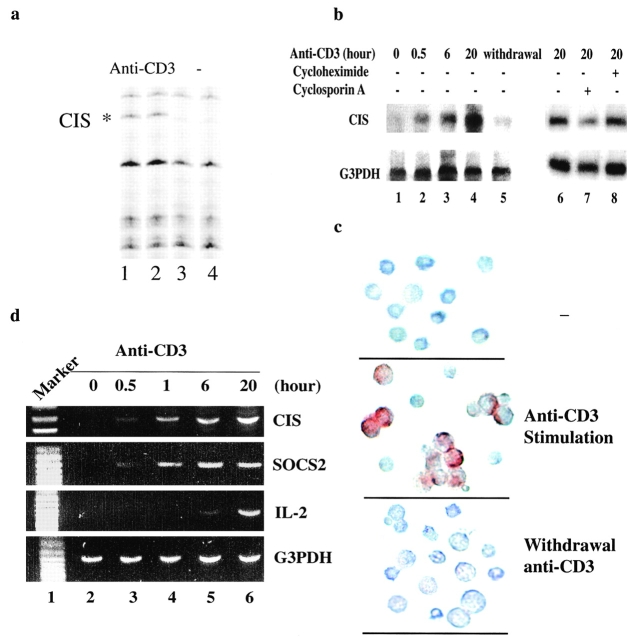
Figure 1.
CIS was induced by TCR activation. (a) Differentially displayed CIS transcript in anti-CD3–stimulated CD4 T cells. (b) Northern analysis of mRNA from CD4 T cells treated with anti-CD3 for different periods of time showing induced expression of CIS (lanes 1–4), and dependence on TCR activation (lane 5). The effect of cycloheximide or cyclosporin A on anti-CD3–induced CIS expression was analyzed by incubation with cyclosporin A together with anti-CD3 or addition of cycloheximide after anti-CD2 stimulation for 6 h (lanes 6–8). Probe specific for G3PDH confirmed that equal amounts of RNA were present in each sample. (c) The expression of CIS in CD4 T cells was analyzed by immunostaining with anti-CIS antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) as described (reference 41). Induced CIS expression was detected in activated T blasts after 20-h stimulation with anti-CD3. Expressed CIS was degraded in 16 h after withdrawal of anti-CD3. (d) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA from CD4 T cells activated with anti-CD3 for different periods of time showing the kinetics of CIS, SOCS2, and IL-2 induction. Primers specific for G3PDH confirmed that equal amounts of RNA were present in each sample.