Figure 6.
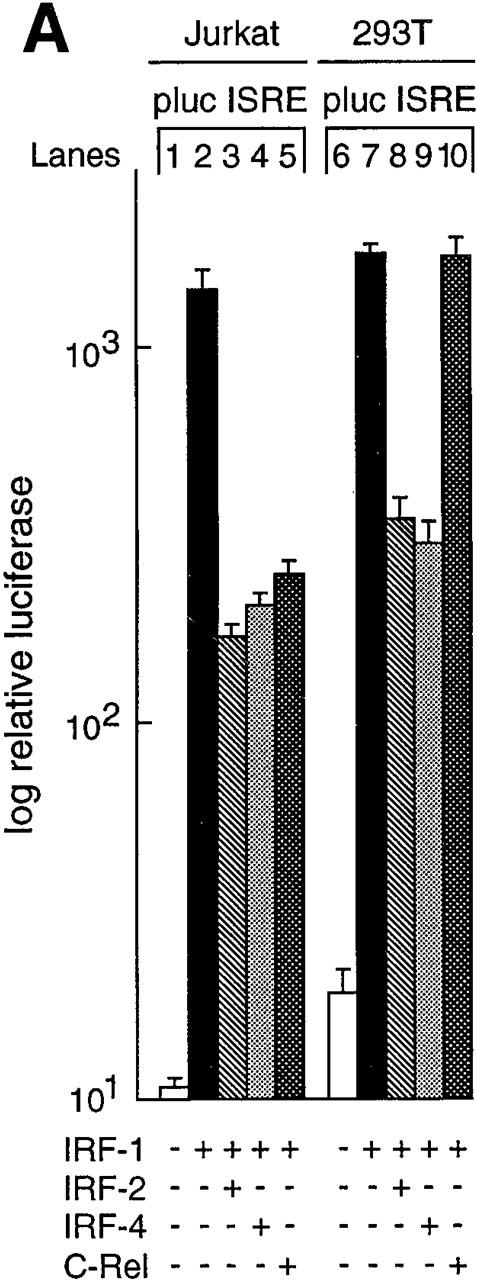
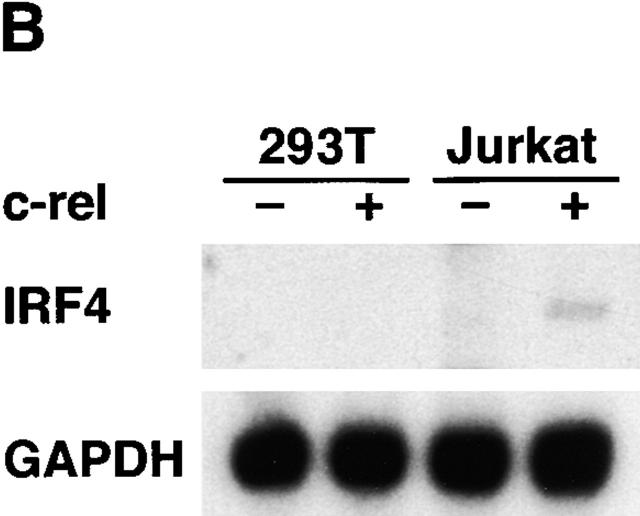
Rel regulation of IRF-1–dependent transcription. (A) Rel repression of IRF-1–dependent transcription is lymphoid specific. Jurkat T cells (lanes 1–5) and 293T fibroblasts (lanes 6–10) were transiently transfected with 2 μg of the ISRE-regulated reporter plasmid plucISRE in the absence (lanes 1 and 6) or presence of an equimolar concentration of expression vectors encoding IRF-1 (lanes 2 and 7) IRF-1 plus IRF-2 (lanes 3 and 8), IRF-1 plus IRF-4 (lanes 4 and 9), or IRF-1 plus c-rel (lanes 5 and 10). Luciferase activity for transfections with vector control (white bars), IRF-1 (black bars), IRF-1 plus IRF-2 (hatched bars), IRF-1 plus IRF-4 (stippled bars), or IRF-1 plus c-rel (cross-hatched bars) represent the mean activity ± SD obtained from four separate sets of transient transfections. (B) Rel repression of IRF-1–regulated transcription in T cells coincides with IRF-4 induction. 10-μg samples of total RNA isolated from Jurkat and 293T cells transiently transfected with 15 μg of pDAMP56 (vector control) or pDAMP56 c-rel after 48 h were analyzed by Northern blot hybridization with murine IRF-4 and rat GAPDH cDNA probes. Filters were exposed to autoradiography for 24 h.