Figure 1.
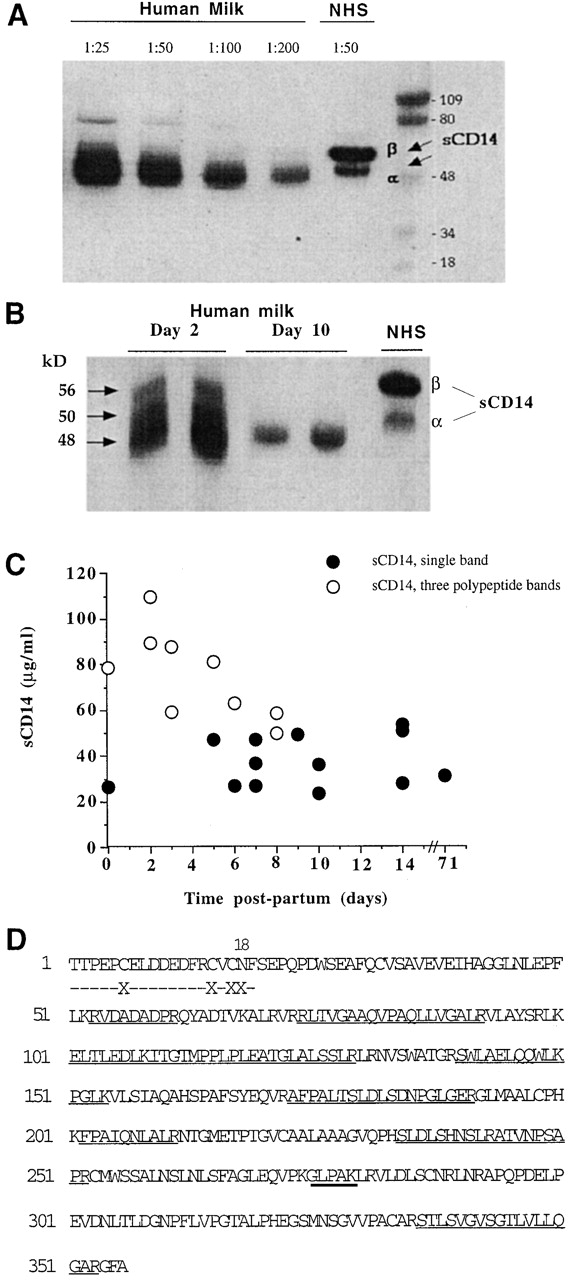
Detection and characterization of sCD14 in human milk. (A) Milk samples (1:25 to 1:200 dilutions) taken after the first week postpartum and normal human serum (NHS) were tested for sCD14 by Western blotting. Shown is the result of one sample representative of 10 donors. (B) Analysis of m-sCD14 in milk samples taken at day 2 or day 10 postpartum from the same mother. Samples from two donors are shown. NHS, normal human serum. (C) m-sCD14 levels determined by ELISA in multiple samples taken from 10 donors at different times postpartum. Values correspond to the mean of triplicate determinations (SD ≤ 6%). The m-sCD14 molecular pattern of each sample was determined by Western blotting and is indicated by the symbols. (D) NH2-terminal sequence (dashed line) and mass spectrometric analysis followed by amino acid sequencing (solid line) of 48-kD m-sCD14 tryptic peptides showing homology with the predicted sequence from monocyte CD14 cDNA. Thick solid line underlines a peptide analyzed only by mass spectrometry. X, not determined.
