Figure 6.
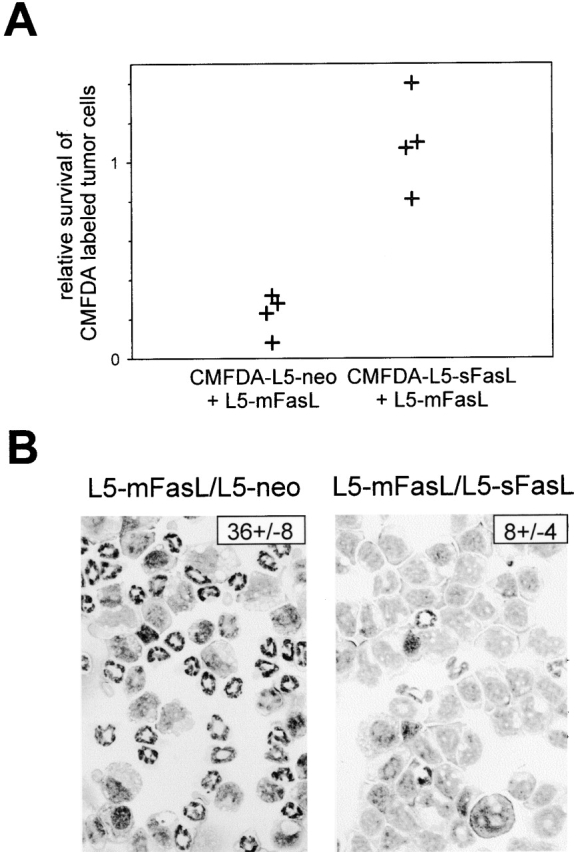
Soluble FasL inhibited the proinflammatory activity of mFasL. (A) DBA/2 mice were injected intraperitoneally with either 2 × 106 PMA plus ionomycin–preactivated or 6 ×106 unactivated, CMFDA-labeled L5-neo, or CMFDA-labeled L5-sFasL cells alone, or as a mixture with 6 × 105 L5-mFasL cells. After 16 h, PECs were isolated and survival of the CMFDA labeled tumor cells was assessed by flow cytometry. The relative rate of tumor cell survival was calculated by dividing the number of cells recovered, when L5-sFasL and L5-neo cells were mixed with L5-mFasL, by the number of cells recovered when L5-sFasL and L5-neo cells were injected alone. Shown are the pooled results from two independent experiments; dots represent relative survival rates of labeled tumor cells per mouse. (B) Neutrophil inflammation was assessed by blind enumeration of the number of neutrophils per 100 PECs in Wright-Giemsa–stained cytospins. A representative field is shown for each group. The number in the top right corner indicates the mean percentage of neutrophils ± SD of three to four mice per group.
