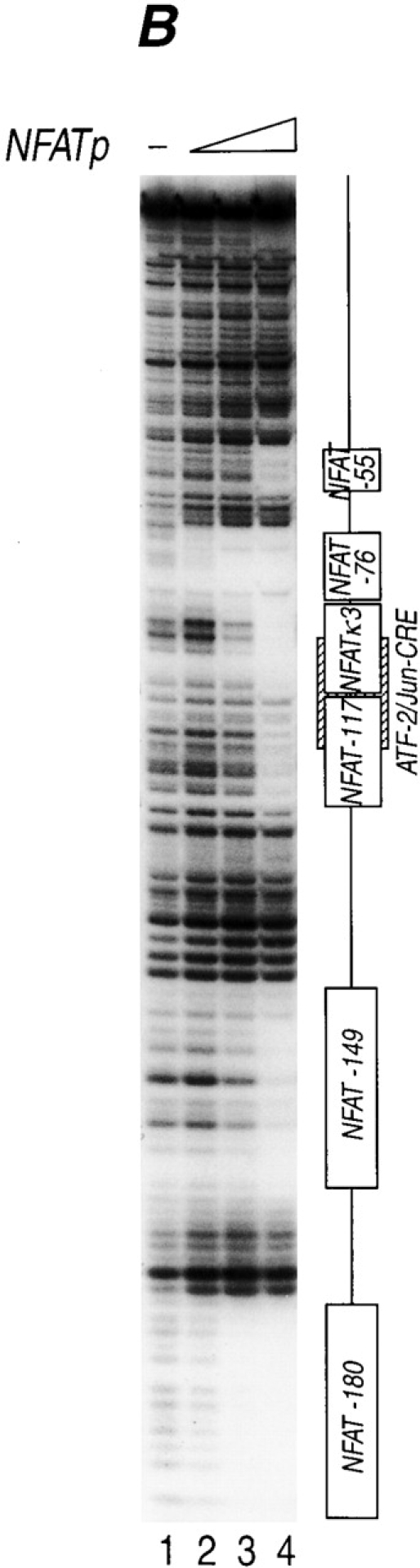
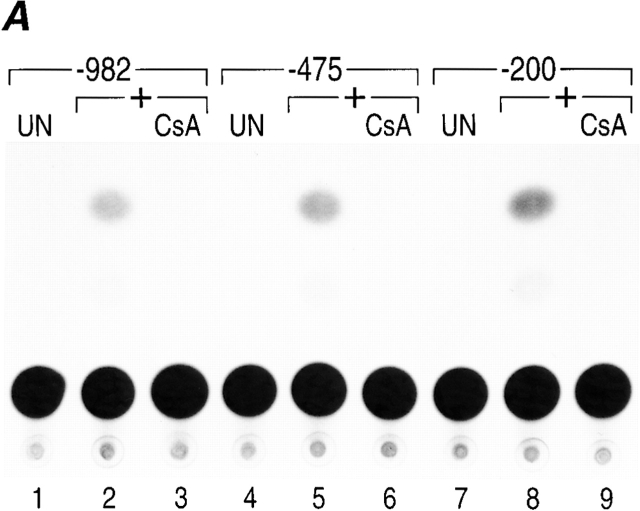
Figure 1.
Murine TNF-α gene expression is dependent upon NFAT. (A) −200 nucleotides upstream of the TNF-α mRNA cap site are sufficient for CsA-sensitive anti-CD3 induction of TNF-α in T cells. The Ar-5 T cell clone was transfected with CAT reporters linked to murine TNF-α promoters containing −200, −475, or −982 nucleotides upstream of the mRNA cap site and treated with anti-CD3 antibody and pretreated with CsA for 10 min as indicated. A representative CAT assay of three independent transfections is shown. Transfections included CMV–β-gal as a control and CAT activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity. (B) NFATp binds to six sites in the TNF-α promoter. Quantitative DNaseI footprinting using the murine TNF-α promoter (−200 to +87 nucleotides relative to the transcription start site) and increasing concentrations of recombinant NFATp (100 ng, 400 ng, and 2 μg) or BSA at 2 μg (–). The NFATp binding sites and the ATF-2/Jun binding site (CRE) are indicated in the drawing at the right.