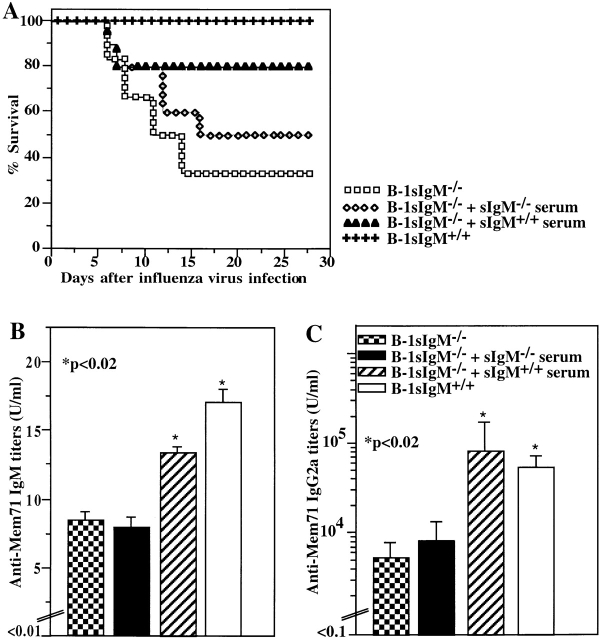
Figure 8.
Reconstitution of natural IgM–deficient chimeras results in increased survival and increased antiviral IgG2a serum titers after influenza virus infection. Lethally irradiated recipients were reconstituted with bone marrow from wild-type mice and PerC cells from sIgM−/− mice (B-1 sIgM−/−). Chimeras received daily injections of 0.5 ml of normal serum (sIgM+/+ serum; n = 10) or IgM-deficient serum (sIgM−/− serum; n = 10) immediately before infection and daily for 5 d after infection. Control mice received both bone marrow and PerC cells from sIgM+/+ mice (B-1 sIgM+/+). (A) Survival from infection with influenza A/Mem71 was monitored daily for 28 d. (B) Mem71-binding serum IgM titers were determined by ELISA in groups (n = 9) of noninfected chimeras after 3 d of daily injections with the indicated type of serum or in controls. Arbitrary units of antivirus Ig per milliliter are shown. (C) Mem71-specific IgG2a titers in the sera of indicated groups of irradiation chimeras were determined at day 8 after infection with influenza A/Mem71 by ELISA. Arbitrary units of antivirus Ig per milliliter are shown.