Figure 7.
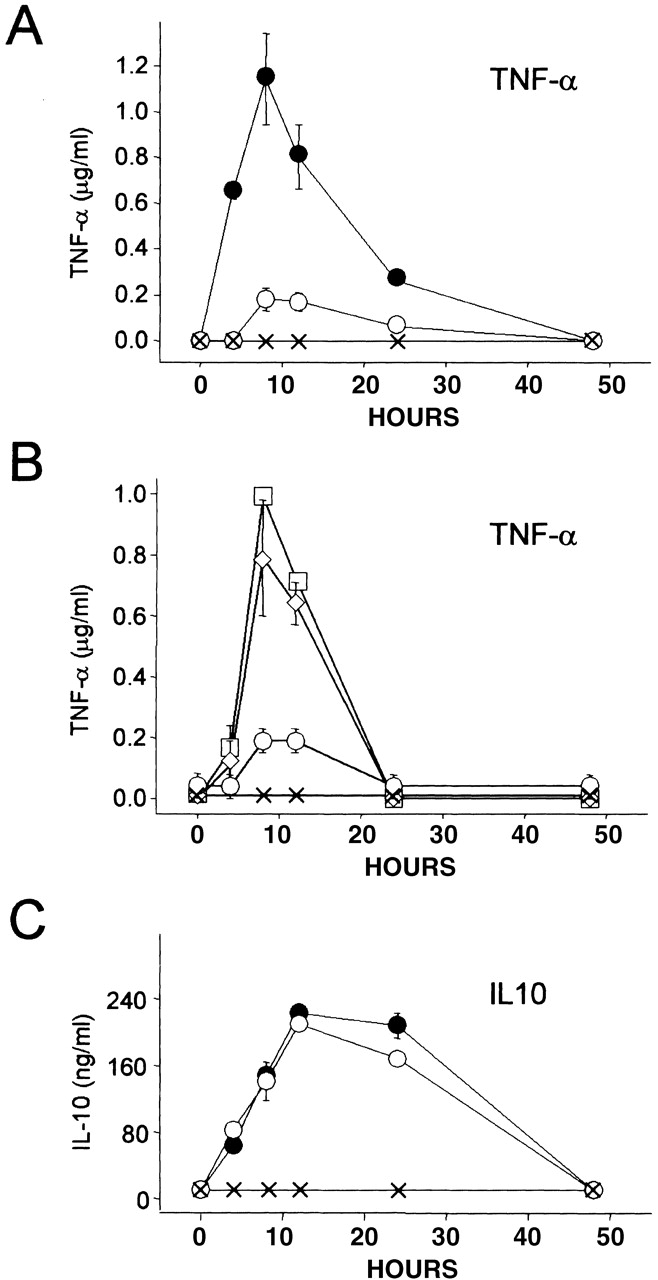
TNF-α and IL-10 production examined in CD43+/+ and CD43−/− Mφ challenged with M. avium. (A) M. avium–induced TNF-α production is significantly impaired in CD43−/− Mφ. Mφ from CD43+/+ (•) and CD43−/− (○) mice were inoculated with M. avium (two bacteria per Mφ), and the supernatants harvested at the indicated times were assayed by ELISA. The levels of TNF-α produced by M. avium–challenged CD43+/+ and CD43−/− Mφ are significantly different at 4, 8, and 12 h (P < 0.001, 0.007, and 0.01, respectively). In the absence of mycobacterial challenge, neither CD43+/+ (×) nor CD43−/− Mφ (not shown) produced TNF-α. (B) Impaired TNF-α production by M. avium–challenged CD43−/− Mφ is restored by Galgp. CD43−/− Mφ were inoculated with M. avium (two bacteria per Mφ) in the absence (○) and presence of 100 (⋄) and 200 (□) μg/ml Galgp. Galgp was tested also at 50 μg/ml, and the resulting TNF-α levels were indistinguishable from levels produced in the absence of added Galgp (○). Note that 200 μg Galgp increases TNF-α to levels of CD43+/+ cells at 8 and 12 h (compare with A). The levels of TNF-α are significantly different for M. avium–challenged CD43−/− Mφ in the absence and presence of 100 and 200 μg/ml Galgp at 8 and 12 h (P < 0.02). Note also that Mφ cultured with Galgp (200 μg/ml) in the absence of mycobacterial challenge (×) did not produce TNF-α. (C) M. avium–dependent IL-10 production is not impaired in CD43−/− Mφ. The Mφ supernatants from A were assayed for IL-10 by ELISA. The levels of IL-10 produced by CD43+/+ (•) and CD43−/− (○) Mφ after inoculation with M. avium are not significantly different at any time point (P values range from 0.06 to 0.85). Neither CD43+/+ (×) nor CD43−/− Mφ (not shown) produced IL-10 in the absence of mycobacterial challenge. Values are mean ± SEM of replicate assays of fractions from three mice of each group.
