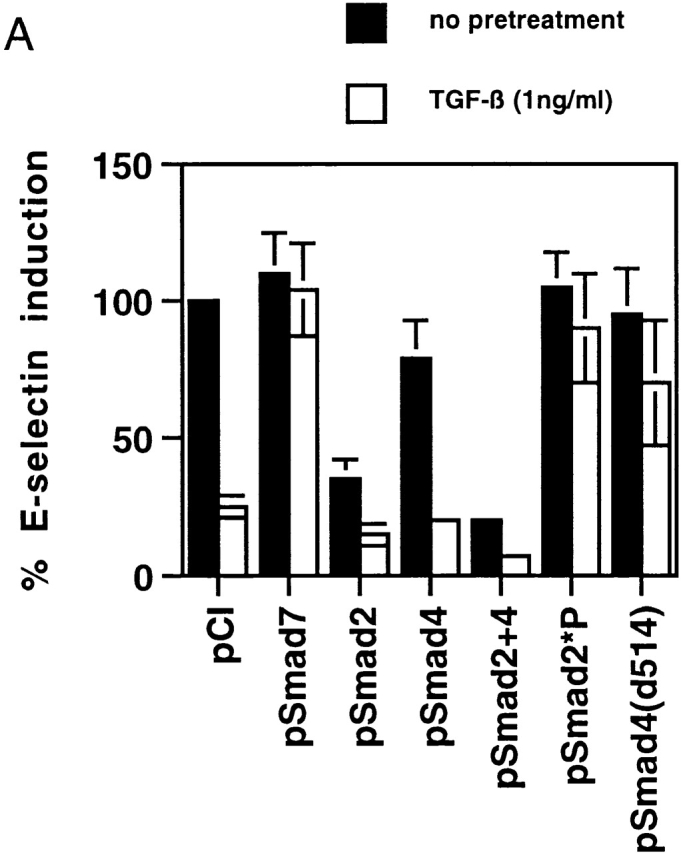
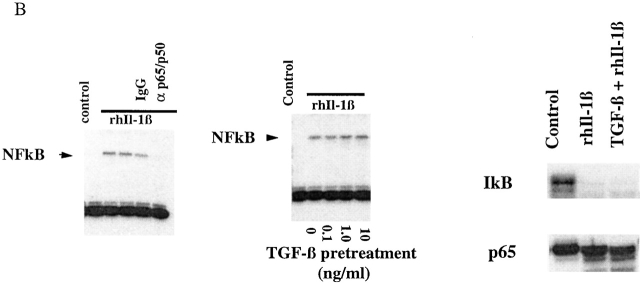
Figure 2.
(A) TGF-β1–mediated inhibition of IL-1β–induced E-selectin expression in endothelial cells is Smad protein dependent. BAECs were transiently cotransfected with the E-selectin promoter construct and the indicated Smad protein expression constructs or an empty expression vector (pCi). The cells were subsequently stimulated for 4 h with TNF-α, with and without 6 h of pretreatment with TGF-β1 at 1 ng/ml. The level of induction of the E-selectin promoter has been normalized to that seen in the absence of TGF-β1 pretreatment (in the presence of the cotransfected empty expression vector) and expressed as 100%. In the presence of cotransfected empty expression vector (pCI), there is a marked inhibition of E-selectin promoter induction by TGF-β1 pretreatment, as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Coexpression of Smad7, an inhibitory Smad protein, or of Smad2*P or Smad4 (d514), which can act as dominant negative inhibitors, markedly attenuates the TGF-β1–mediated inhibition. In contrast, coexpression of wild-type Smad2, Smad4, or both Smad2 and -4 significantly enhances the level of inhibition seen and is able to induce varying levels of inhibition even in the absence of exogenous TGF-β1 pretreatment. All of the Smad expression constructs encode epitope-tagged species that were expressed at comparable levels as monitored by immunoblot (data not shown). (B) Cytokine-induced activation of NFκB appears preserved in the presence of TGF-β1 pretreatment. HUVEC monolayers were treated with 10 U/ml of rhIL-1β for 30 min and lysed, and a nuclear extract was prepared. Specific NFκB-mediated DNA binding activity was assessed by mobility shift assay and compared with that present in unstimulated HUVEC. As shown in the left panel, there is a specific shifted band present in the rhIL-1β–treated lanes but not in the control (untreated) lane that can be abolished by immunodepletion of the extract with a mixture of anti-p65/antip50 antisera but not nonspecific IgG. As shown in the middle panel, rhIL-1β–induced, NFκB-mediated DNA binding activity (as assessed by this gel shift) appears preserved even in the presence of TGF-β pretreatment. The panels at the right represent immunoblots for IκB and P65 protein levels. The former is markedly depleted by rhIL-1β treatment, even in the presence of TGF-β1 pretreatment. p65 levels appeared stable under these conditions. These findings suggest that IκB degradation and NFκB-mediated DNA binding are not affected by TGF-β1 pretreatment in HUVECs.