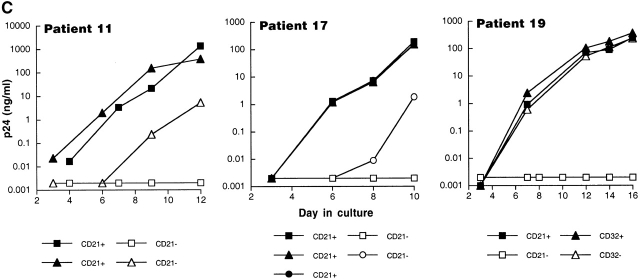
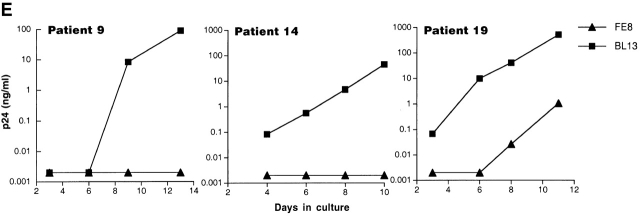
Figure 3.
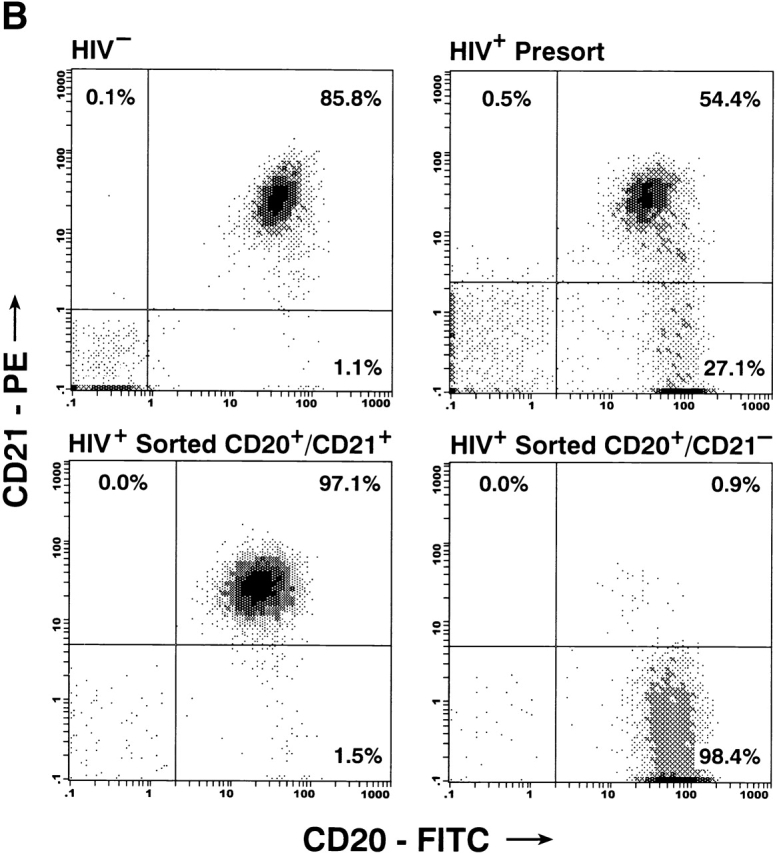
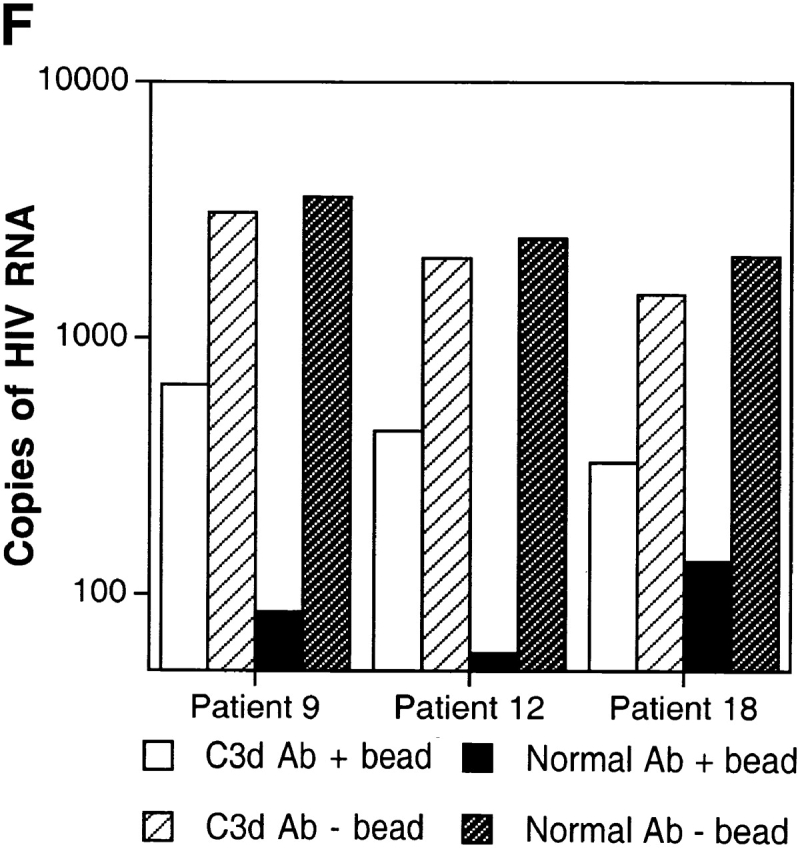
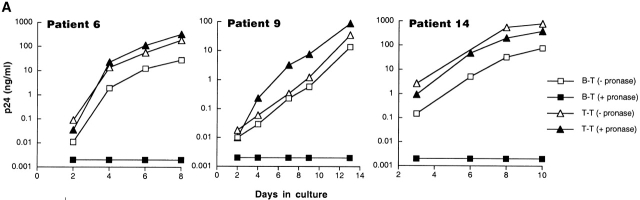
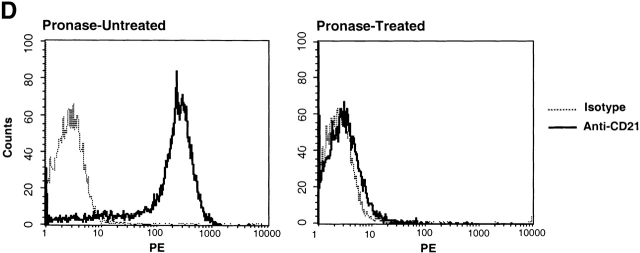
Characterization of the replication-competent virus associated with PBMC-derived B cells of HIV-infected patients. (A) B cells and T cells isolated from three HIV-infected individuals were pretreated with pronase followed by coculture with indicator T cells. (B, top) Flow cytometric comparison of CD21 expression on representative HIV-negative B cells and presorted B cells of patient 17, followed by (B, bottom) post-sorted CD20+/CD21+ and CD20+/CD21− fractions of patient 17. (C) B cells of three HIV-infected patients sorted into CD21+ and CD21− fractions (and CD32+ versus CD32− fractions in the case of patient 19) and cocultured with indicator T cells. Colors identify the sorted fraction and symbols identify the number of coculture wells plated for a given sorted fraction. (D) Flow cytometric comparison of CD21 expression on pronase-treated and -untreated B cells of patient 9. (E) B cells of three HIV-infected patients preincubated with mAbs FE8 and BL13 and cocultured with indicator T cells. (F) FE8-displaced HIV from 2 × 106 B cells of three HIV-infected patients, treated with rabbit anti–human C3d (C3d Ab) or normal rabbit serum (Normal Ab), and captured with magnetized anti-rabbit antibodies. Fractions captured on magnet (+ bead) and fractions not captured (− bead) were tested for HIV-1 RNA by bDNA.