Figure 4.
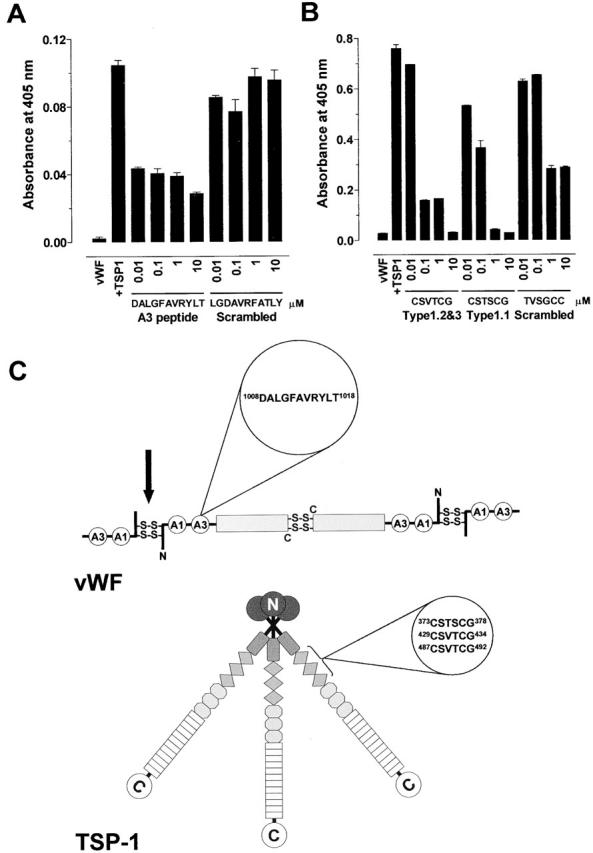
Characterization of the binding sites on TSP-1 and vWF. (A) Platelet TSP-1 (10 μg/ml) was incubated with Hepes-buffered saline containing 1 mM CaCl2 and vWF A3 domain peptide DALGFAVRYLT or scrambled peptide LGDAVRFATLY (0.01 to 100 μM) for 10 min at 37°C. The reaction was started by addition of purified vWF (2 μg/ml) and incubated for 60 min at 37°C. The vWF was labeled with MPB and detected with streptavidin peroxidase. The bars and errors are the mean and SD of triplicate determinations. (B) Purified vWF (2 μg/ml) was incubated with Hepes-buffered saline containing 1 mM CaCl2 and TSP-1 type 1 peptides CSVTCG, CSTSCG, or scrambled peptide TVSGCC (0.01 to 100 μM) for 10 min at 37°C. The reaction was started by addition of platelet TSP-1 (10 μg/ml) and incubated for 60 min at 37°C. The vWF was labeled with MPB and detected with streptavidin peroxidase. The bars and errors are the mean and SD of triplicate determinations. (C) Cartoon of the quaternary structures of vWF and TSP-1 and position of the amino acid sequences that mediate their interaction. Dimers of vWF are assembled from subunits via disulfide bridges between cysteine residues located in the COOH-terminal regions. Multimers are formed from dimers by interdimeric disulfide linking of NH2-terminal domains in a parallel orientation. The A1 and A3 domains of the vWF subunit are indicated. We propose that TSP-1 reduces the interdimeric disulfide bonds (black arrow). The TSP-1 subunit contains a unique heparin-binding domain at the NH2 terminus, followed by a connecting region that link three subunits via interchain disulfide bonds, a procollagen-like module, three properdin-like or type 1 modules, three epidermal growth factor–like or type 2 modules, 12 unique calcium-binding loops (or seven type 3 repeats), and a unique COOH-terminal globular domain.
