Figure 3.
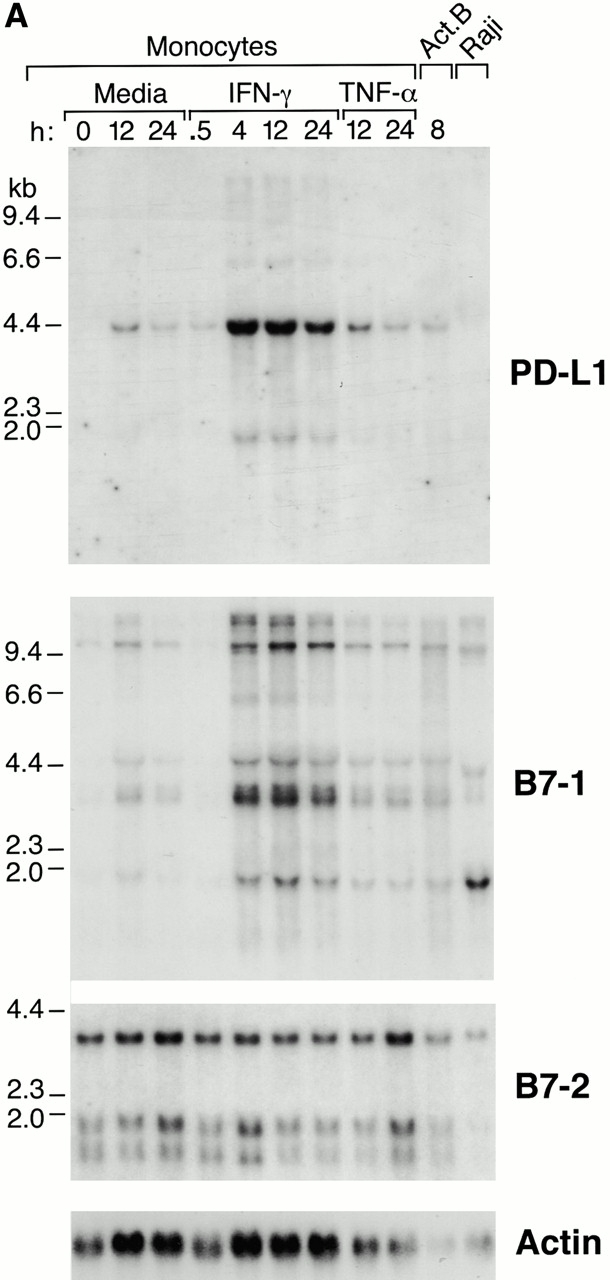
Expression of PD-L1 in antigen-presenting cells and murine tissues. (A) Northern blot analysis of total RNA of human peripheral blood monocytes stimulated with 500 U/ml human IFN-γ, 100 U/ml human TNF-α, or media alone, and anti-Ig–activated human B cells, with human PD-L1, B7-1, B7-2, and β-actin cDNA probes. Cells were prepared and stimulated as described (reference 28). Act.B, actinomycin B. (B) Isolated human peripheral blood dendritic cells (DC) were cultured in either human GM-CSF alone (gray bars) or in GM-CSF, LPS, and IFN-γ (black bars) for 4 or 20 h, after which RNA was isolated for quantitative (real time) PCR analysis. Fluorescence is plotted as a ratio of PD-L1, B7-1, or B7-2 signal to the GAPDH signal. (C) Northern blot analysis of human keratinocyte total RNA with a human PD-L1 cDNA probe. Keratinocytes were isolated and activated with PMA and IFN-γ, as described previously (reference 10). (D) Northern blot analysis of murine tissue polyA+ RNAs (Ambion) with a murine PD-L1 cDNA probe. (E) The human PD-L1 gene was amplified by PCR from monochromosomal somatic cell hybrid genomic DNAs containing the indicated human chromosome as well as hamster, murine, and human genomic DNAs.




