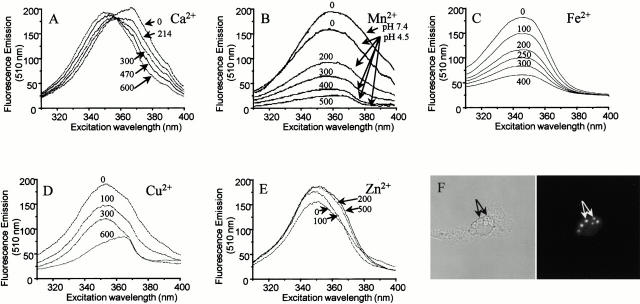
Figure 2.
(A–E) Spectral properties of zymosan–FF6 particles in suspension. (A) Zymosan–FF6 particles were added to medium containing 140 mM KCl, 20 mM Hepes-Na (pH 7.4), and 500 μM EGTA, and the excitation spectrum was acquired with emission at 510 nm. Increasing amounts of Ca2+ were then added (total concentrations indicated) and fluorescence was recorded as above. (B–E) Zymosan–FF6 particles were added to medium containing 500 μM EGTA and 500 μM Ca2+ buffered at pH 7.4 or 4.5, as indicated, and excitation spectra were acquired (emission = 510 nm). Increasing amounts of Mn2+ (B), Fe2+ (C), Cu2+ (D), or Zn2+ (E) were then added (total concentrations indicated) and the effects of the divalent cations on zymosan–FF6 fluorescence were recorded. (F) Fluorescence properties of zymosan–FF6 particles ingested by macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages plated on coverslips were bathed in Ca2+-free medium and allowed to ingest zymosan–FF6 particles for 30 min at 37°C. Coverslips were mounted in thermoregulated chambers and examined using differential interference contrast optics (left) and epifluorescence with excitation at 360 nm and emission at 535 nm (right). The location of zymosan–FF6 particles is indicated by arrows.