Figure 3.
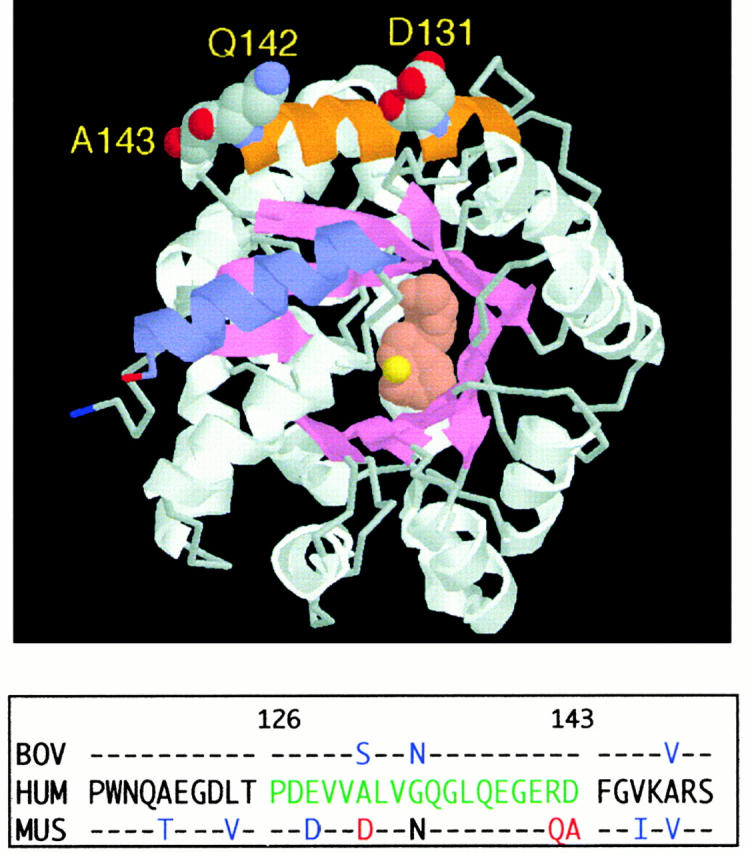
Location of the α2 helix (CD26 binding site) in the murine ADA crystal structure. The RasMol model is based on coordinates, as reported (reference 44). The α2 helix (residues 126–143) is shown in orange, with space-filling display of residues D131, Q142, and A143. For orientation, the COOH-terminal helix (residues 337–351) is shown in blue. Bound inhibitor (rose) and the zinc ion (yellow) are space-filling structures at the active site. The panel below the model compares the partial amino acid sequences (residues 115–150) of human (HUM), murine (MUS), and bovine (BOV) ADA. Amino acids 126–143 of human ADA, green letters; amino acids D131, Q142, and A143 of murine ADA, red letters; other amino acids of bovine and murine ADA that differ from the human sequence, blue letters.
