Figure 5.
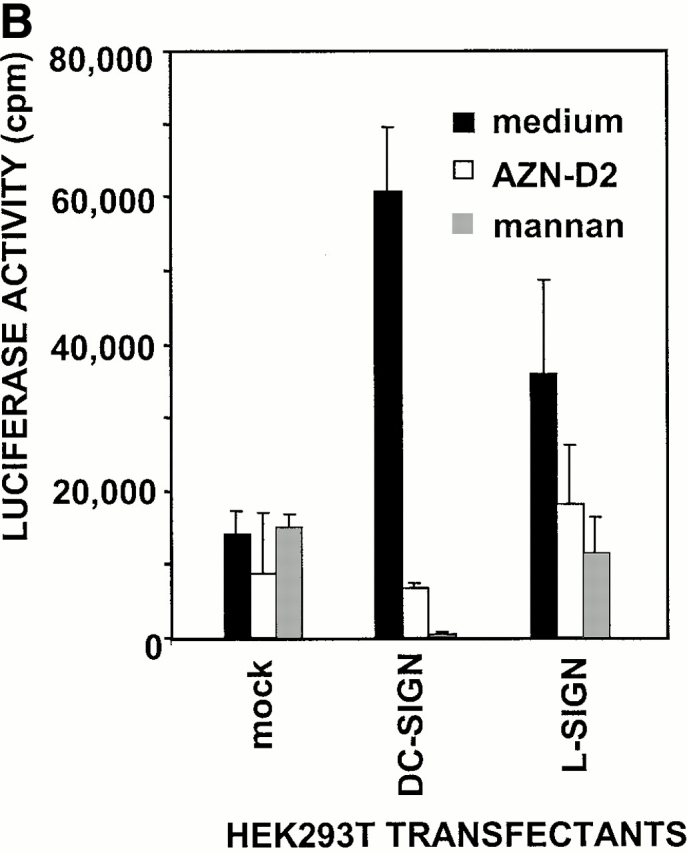
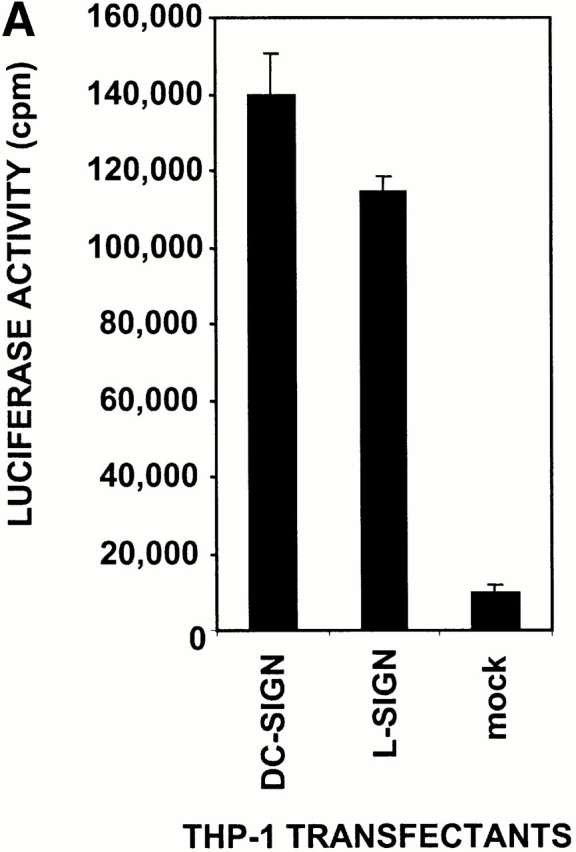
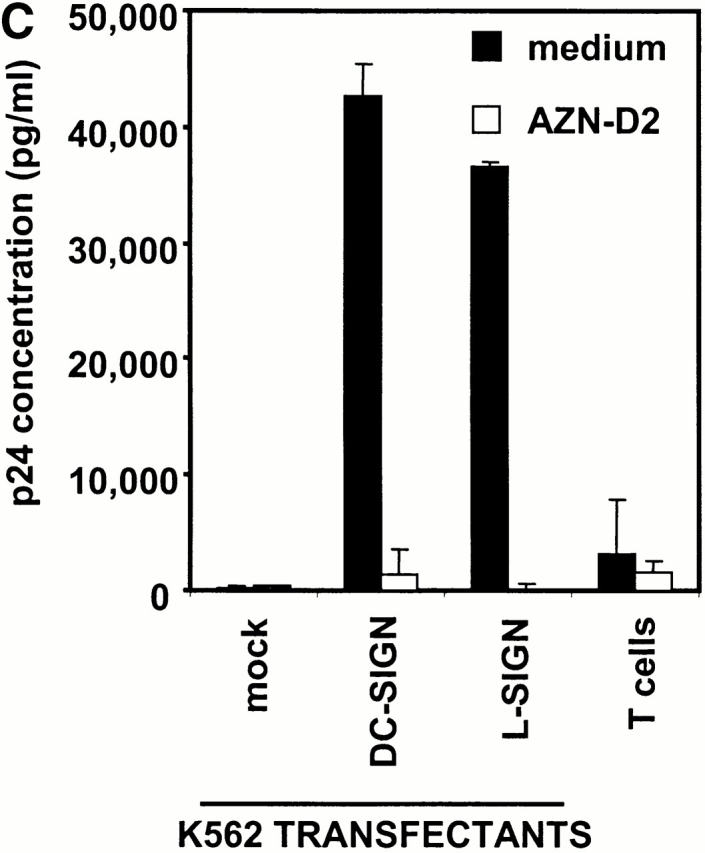
L-SIGN captures and enhances infection of T cells with HIV-1 in trans. (A) L-SIGN captures HIV-1 and transmits it to target cells. Stable DC-SIGN– or L-SIGN–expressing THP-1 transfectants were preincubated with HIV-luc/JRFL pseudovirions to allow capture of the virus. Cells were washed and THP-1 transfectants were cocultured with Hut/CCR5 target cells. Cell lysates were obtained after 3 d and analyzed for luciferase activity. For each of the coculture conditions employed, mock infected controls were uniformly <100 cps in activity. Each data set represents the mean of four separate wells of infected cells. One representative experiment out of two is shown. (B) L-SIGN enhances infection of T cells by pseudotyped HIV-1. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with cDNA encoding DC-SIGN, L-SIGN, or empty vector. Control cells were preincubated with 20 μg/ml AZN-D2 or 20 μg/ml mannan. Low amounts of pseudotyped HIV-1ADA were added together with activated T cells as described previously (reference 1). Infectivity was determined after 2 d by measuring luciferase activity. One representative experiment of two performed is shown. Each experiment was done in triplicate wells. (C) L-SIGN enhances infection of T cells by replication competent HIV-1. Stable K562 transfectants of both L-SIGN and DC-SIGN were incubated with low virus concentrations of replication-competent M-tropic strain HIV-1JR-CSF (TCID50 100/ml). To determine the specificity, cells were preincubated with AZN-D2 (20 μg/ml). After 2 h, activated T cells were added as described previously (reference 2). Culture supernatants were collected at day 14 after K562-T cell coculture and HIV-1 production was measured using ELISA to determine p24 antigen levels. In control experiments, the same amount of virus was added directly to T cells. One representative experiment out of three is shown. Each data set represents the mean of three separate wells of infected cells.
