Figure 3.
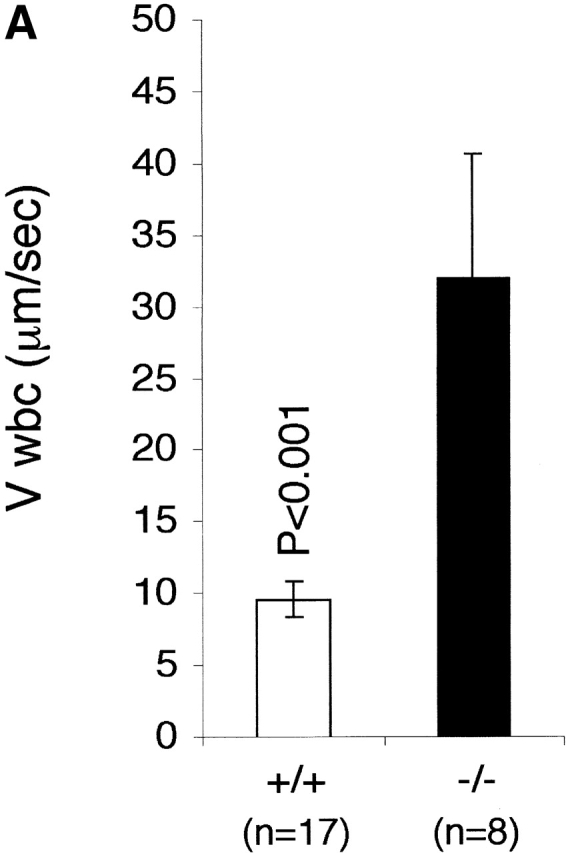
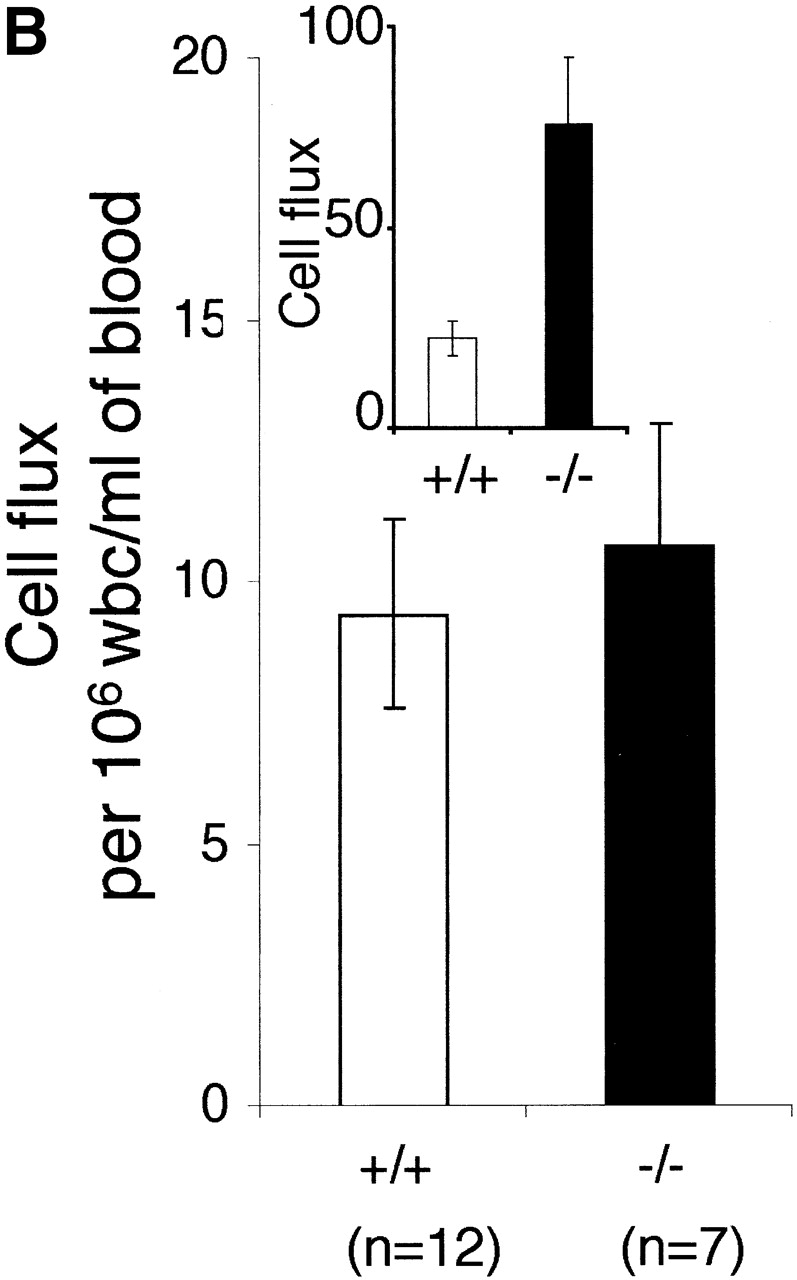
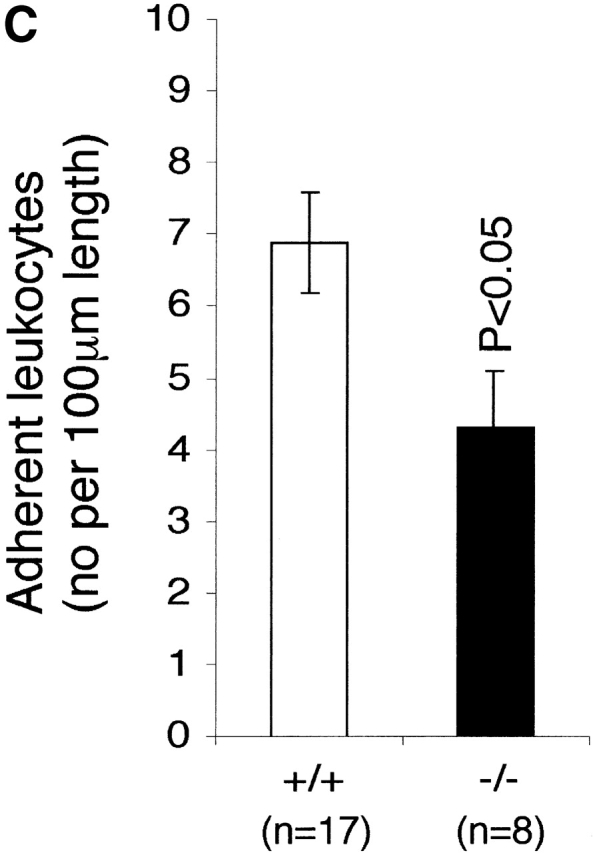
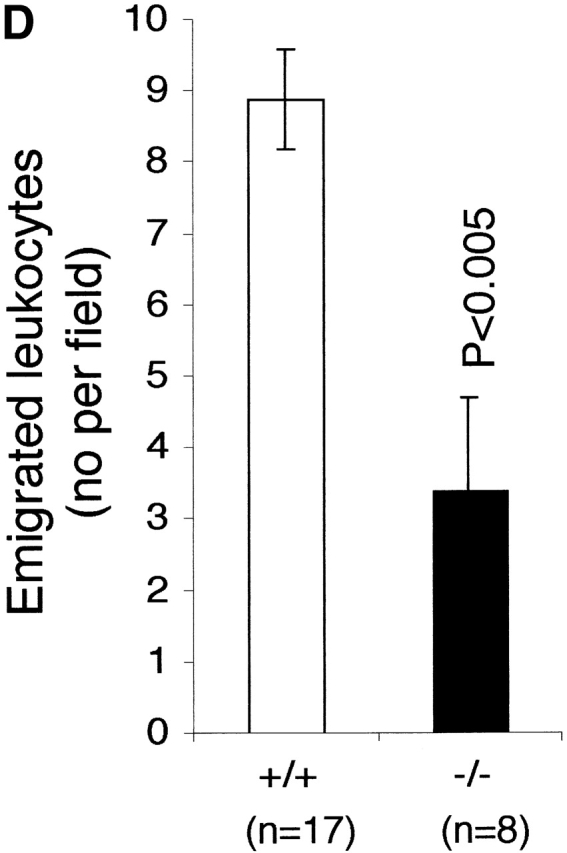
The effect of LFA-1 deficiency on neutrophil rolling, adhesion, and transmigration as detected by intravital microscopy. A comparison in LFA-1+/+ and −/− mice of leukocyte (A) velocity (VWBC); (B) integrated cell flux (i.e., cell flux per 106 leukocytes per milliliter of blood). Inset, basic cell flux (cells per min); (C) cell adhesion; (D) emigrated leukocytes per field (“field” represents cells within 50-μm distance from a 100-μm segment of vessel). The neutrophils from LFA-1−/− mice have a higher velocity than those from LFA-1+/+ mice indicating a role for LFA-1 in neutrophil rolling. Because LFA-1 does not alter the cell flux (frequency of contact with endothelium), it must be decreasing the velocity by transiently stabilizing the rolling cells. A lack of LFA-1 is also reflected in lower adhesion per 100-μm length of mesenteric vessel and decreased emigration from the vasculature by the LFA-1−/− as compared with LFA-1+/+ neutrophils. Data are reported as mean ± SEM.
