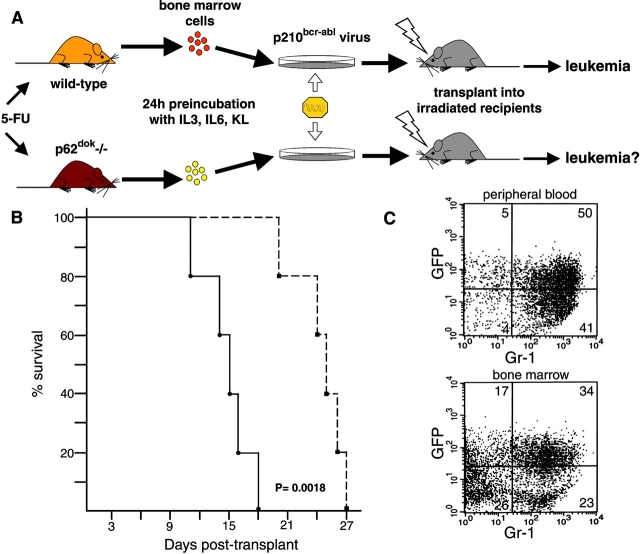
Figure 6.
Retroviral transduction of p210bcr-abl results in the transformation of p62dok−/− bone marrow cells. (A) Schematic representation of the protocol for retroviral transduction of bone marrow and subsequent reconstitution into lethally irradiated recipients (reference 27). (B) Survival of 129/Sv wild-type mice receiving transduced bone marrow cells derived from wild-type (filled square and dashed line) and p62dok−/− (filled circle and solid line) mice. Log rank statistical analysis was performed to obtain P. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood (top), and bone marrow cells (bottom), from a mouse transplanted with p210bcr-abl transduced p62dok−/− bone marrow cells, using a granulocyte surface marker (Gr-1). In the peripheral blood, almost all the infected cells (cells expressing GFP) coexpress the myeloid-specific marker. In the bone marrow, ∼50% of the cells express GFP and >60% of these are Gr-1 positive. A similar immunophenotypical pattern was observed in mice transplanted with wild-type–derived bone marrow (not shown).