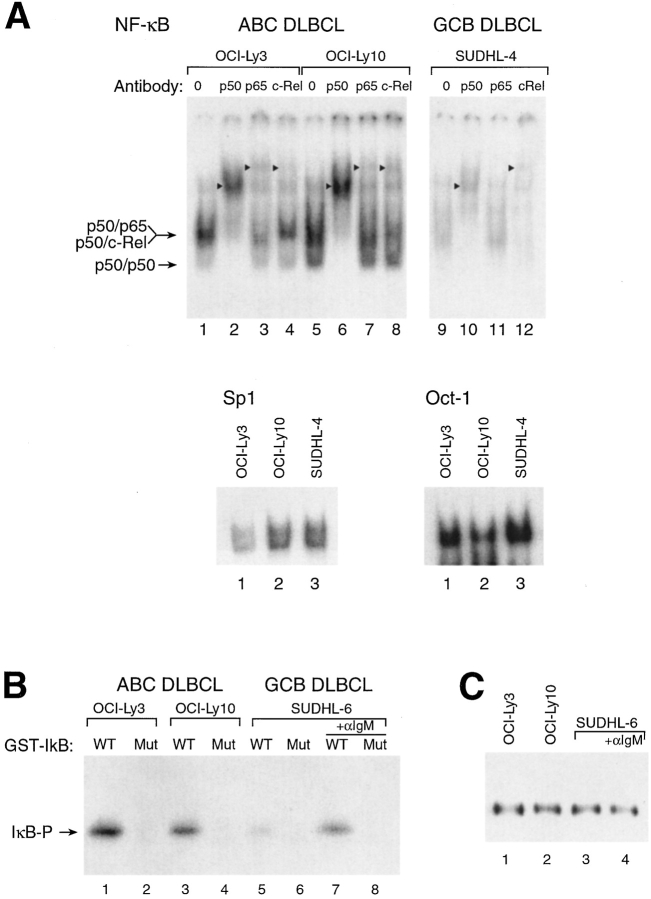
Figure 2.
NF-κB and IKK kinase are constitutively active in ABC DLBCL but not GCB DLBCL cell lines. (A) EMSAs of nuclear extracts from DLBCL cell lines for NF-κB DNA-binding activity. Supershifting antibodies are indicated, as is the mobility of NF-κB heterodimers. Arrowheads indicate the position of supershifted bands. The identity of the p50/p50 homodimer species was established by comparison with extracts of cells transfected with (and overexpressing) p50 (data not shown). EMSAs using Oct-1 and Sp1 probes showed no increased binding activity in ABC DLBCL lines relative to GCB DLBCL lines. Equivalent amounts of protein (10 μg) were used for all reactions. Comparable results were obtained with the GCB DLBCL line SUDHL-6 (data not shown). (B) IKK kinase assay of anti-IKKγ immune complexes from DLBCL cell lines. GST-IκBα (amino acids 1–72) was substrate as follows: WT, wild-type IκBα amino acids 1–72; Mut, IκBα amino acids 1–72 with phosphoacceptor serine residues 32 and 36 substituted by glycine and alanine, respectively. Where indicated, SUDHL-6 cells were activated with anti-IgM (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) for 10 min before extraction. (C) Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitated IKKγ complexes used in B. Western blots were developed with an antibody to IKKα.