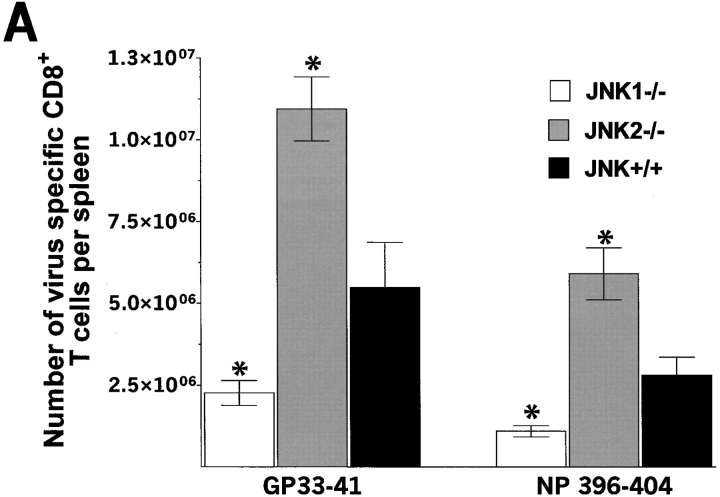
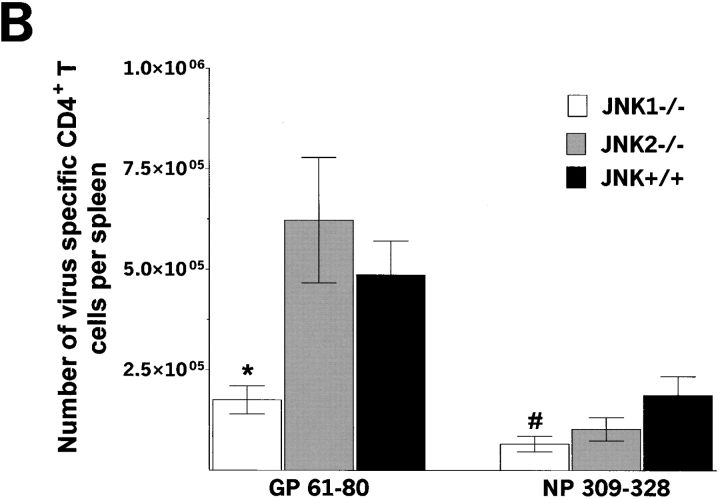
Figure 3.
The number of virus-specific CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells is lower in JNK1−/− mice than in either JNK2−/− or JNK+/+ mice after LCMV infection. JNK1−/−, JNK2−/−, and JNK+/+ mice were injected intraperitoneally with LCMV ARM, 2 × 105 PFU. 8 d after infection, spleen were processed and stimulated for 5 h in vitro with virus-specific peptide GP aa 33–41, NP aa 396–404, GP aa 61–80, or NP aa 309–328. Cells were then stained for surface CD4 or CD8 and intracellular IFN-γ molecules. The number of virus-specific T cells was calculated from the number of total spleen cells obtained per animal. Data represent average values obtained from three animals per group and are representative of two independent experiments. (A) CD8+ T cells; (B) CD4+ T cells. *P < 0.05 #P = 0.052 when compared with JNK+/+.