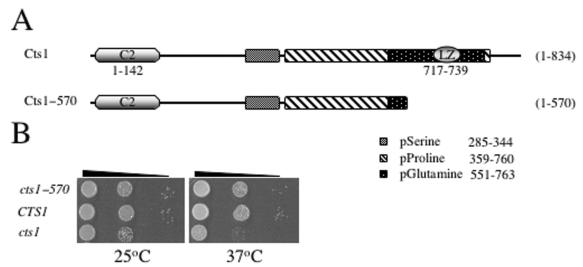
FIG. 3.
Growth of cts1Δ mutants is temperature sensitive. (A) Diagram of the domain structure of Cts1 showing the amino-terminal C2 domain (C2); the serine, proline, or glutamine repeat regions (hatched); and the carboxy-terminal leucine zipper region (LZ). The amino acid positions for each repeat or domain are indicated. The cts1Δ allele completely disrupts the ORF of CTS1, resulting in the absence of Cts1 protein production, while the cts1-570::nat allele truncates 264 amino acids from the C terminus. (B) cts1Δ confers a growth defect. The isogenic wild-type (JEC21) and cts1Δ (DSF45) and cts1-570 (DSF22) mutant strains were serially diluted and grown on YPD medium for 3 days at 25 or 37°C.