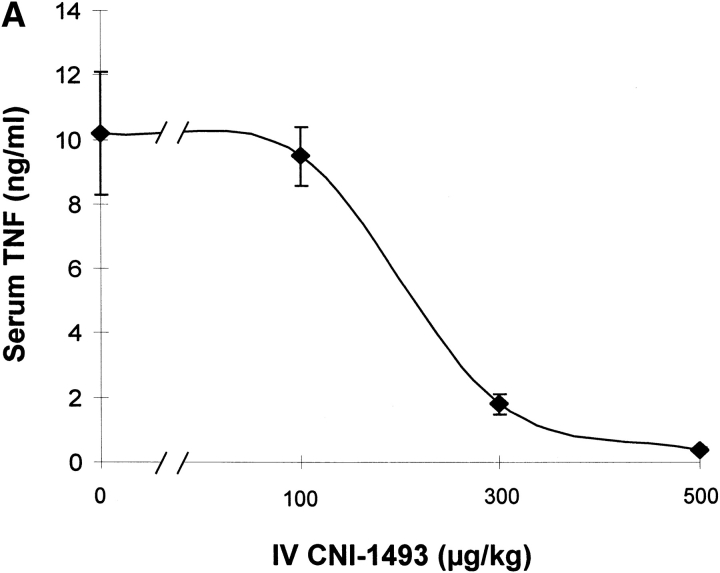
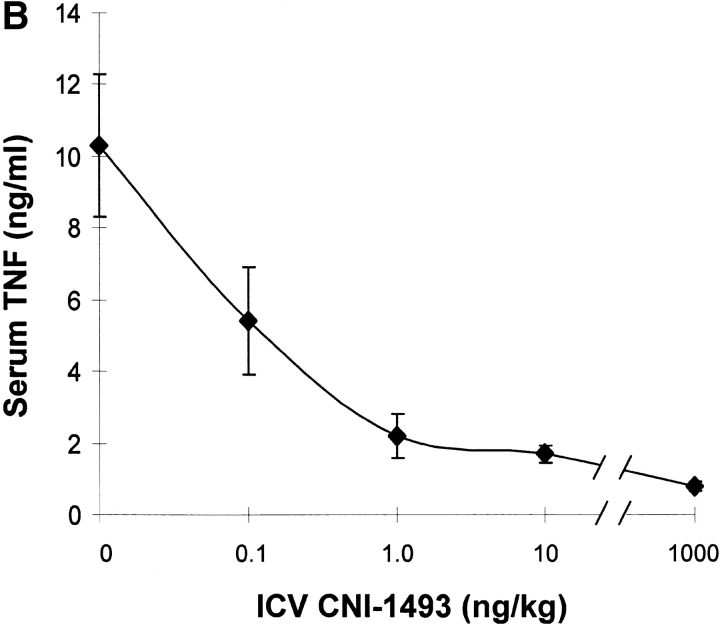
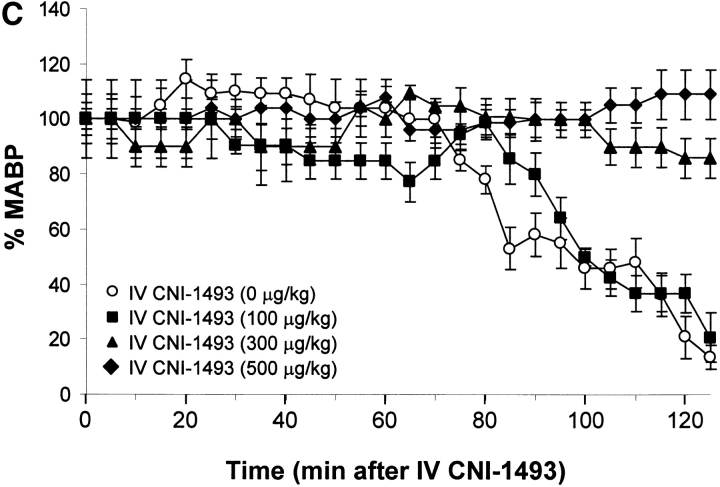
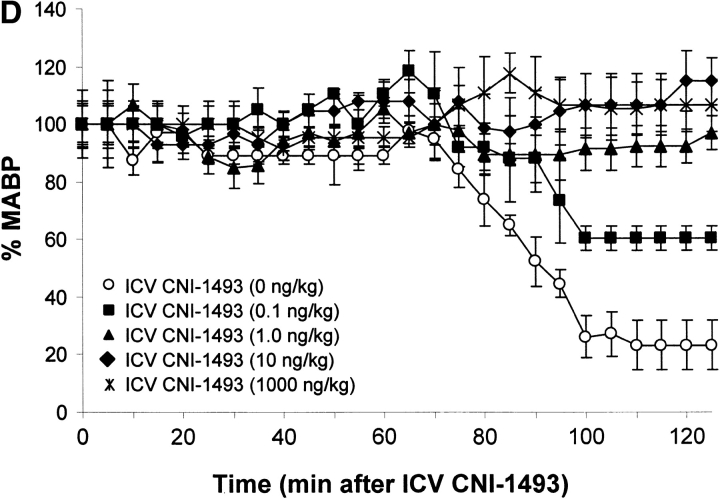
Figure 1.
CNI-1493 (intravenous or i.c.v.) inhibits endotoxin-induced hypotension and attenuates serum TNF. (A) CNI-1493 was given intravenously in the doses shown; endotoxin (15 mg/kg, intravenously) was administered 60 min later. After 1 h, blood was collected via carotid artery catheter, and serum prepared for TNF assays. (B) CNI-1493 was given i.c.v. in the doses shown; endotoxin (15 mg/kg, intravenously) was administered 60 min later. After 1 h, blood was collected via carotid artery catheter, and serum prepared for TNF assays. (C) Intravenous injection of CNI-1493 60 min before endotoxin exposure prevented endotoxic shock. 1 h after exposure to a lethal dose of LPS (15 mg/kg), vehicle-treated endotoxemic rats developed significant LPS-induced hypotension. Intravenous administration of CNI-1493, in doses of 300 or 500 mg/kg, given 60 min before endotoxin exposure significantly prevented the development of LPS-induced hypotension. (D) i.c.v. injection of CNI-1493 60 min before endotoxin exposure prevented endotoxin-induced shock. 1 h after exposure to a lethal dose of LPS (15 mg/kg), vehicle-treated endotoxemic rats developed significant LPS-induced hypotension. i.c.v. doses of CNI-1493 (1,000, 10, 1.0, and 0.1 ng/kg) given 60 min before endotoxin exposure significantly prevented the development of LPS-induced hypotension.