Figure 2.
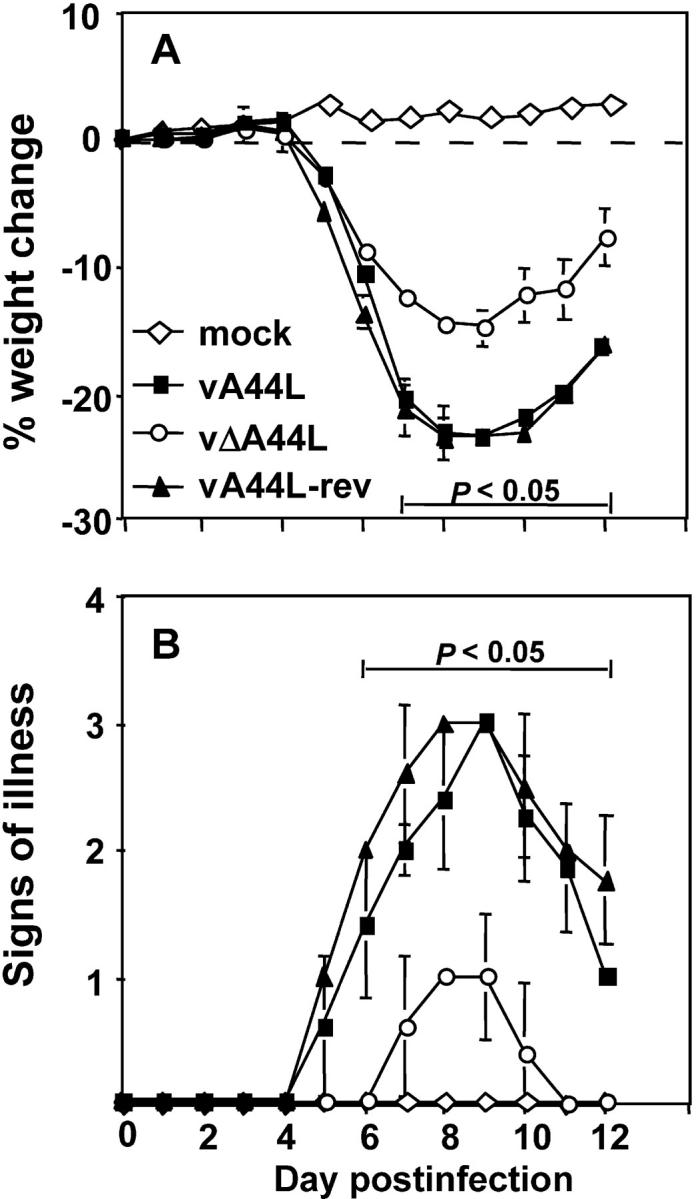
Deletion of A44L attenuates VV WR infection in a murine intranasal model. Groups of five BALB/c mice were mock-infected (⋄) or infected with 104 PFU of vA44L (▪), vΔA44L (○), or A44L-rev (▴). (A) Mice were weighed daily and results are expressed as the mean percentage weight change of each group ± SEM compared with the weight immediately before infection. (B) Animals were monitored daily for signs of illness, scored from 1 to 4. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from five mice. P values were determined using the Student's t test and indicate the mean % weight changes or signs of illness of mice infected with vΔA44L that were significantly different from both those of mice infected with vA44L or A44L-rev.
