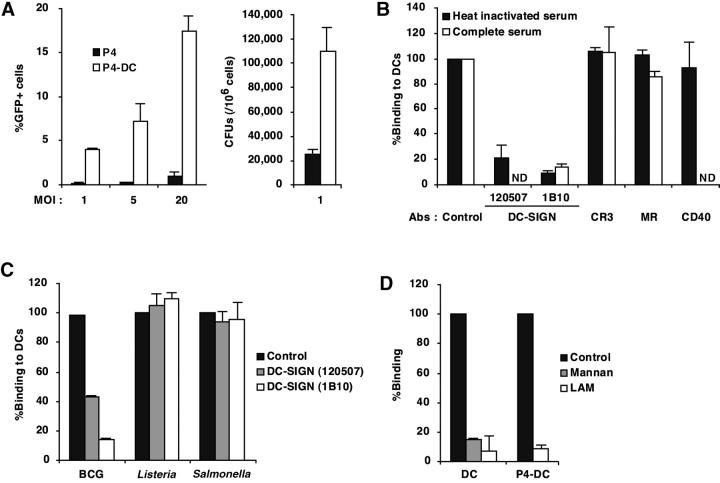
Figure 1.
M. tuberculosis binds to DC-SIGN. (A) Epithelial HeLa-derived P4 cells expressing or not DC-SIGN (P4-DC and P4, respectively) were infected with GFP expressing (GFP+) M. tuberculosis H37Rv at different MOIs. Bacteria binding was evaluated by flow cytometry (left panel) and CFU counts (right panel). Data represent means (±SD) of three separate experiments. (B) MDDCs were infected with GFP-M. tuberculosis H37Rv at an MOI of 1 bacterium per cell in the presence or not of 10% complete human serum, either directly (control) or after preincubation with 10 μg/ml of mAbs directed against CR3/CD11b, MR, CD40, or DC-SIGN. Bacteria binding was assessed by flow cytometry. Preincubation with the corresponding isotype controls led to no significant inhibition of mycobacteria binding (not shown). Data were expressed as percentages of binding relative to control values (100%, no mAb), and means (±SD) of three independent experiments are shown. (C) MDDCs were infected with GFP-M. bovis BCG, Salmonella typhimurium (clinical isolate), or Listeria monocytogenes (clinical isolate) and subjected to the binding assay. In experiments using S. typhimurium and L. monocytogenes, infected cells were plated out onto agar medium and CFUs were scored after 24 h at 37°C. Data are expressed as in B. (D) M. tuberculosis binding to DC-SIGN is inhibited by LAM. Cells were pretreated for 1 h at 4°C with 10 μg/ml mannan as control, or with 10 μg/ml LAM, and subjected to the binding assay. Data are expressed as in B.