Figure 2.
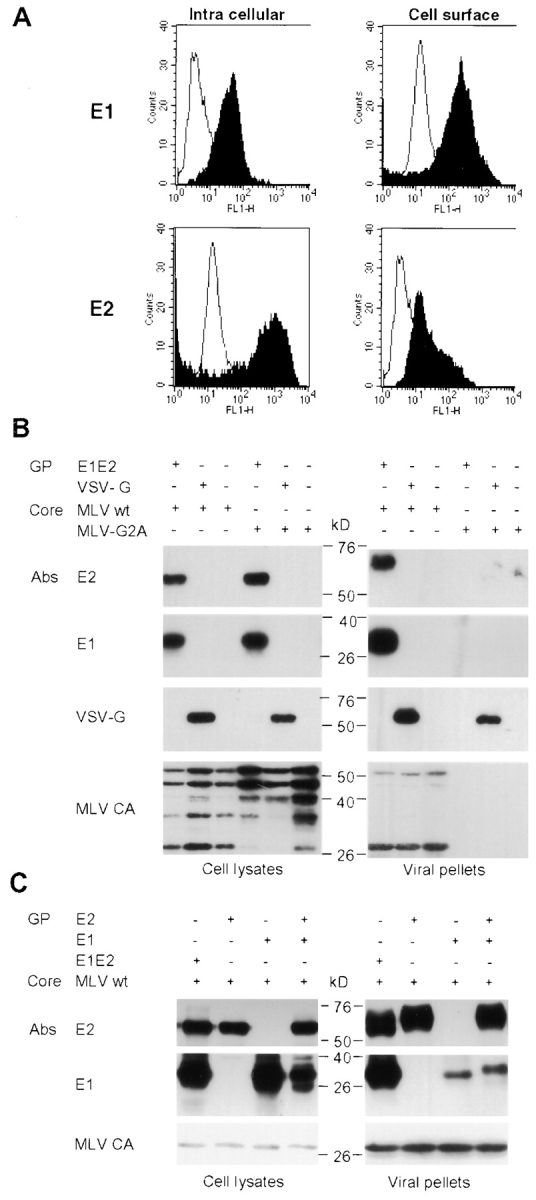
Assembly of HCV pseudo-particles. (A) Detection of E2 glycoproteins by flow cytometry. E1E2-transfected 293T cells were or were not permeabilized before staining with A4 or H53 monoclonal antibodies against E1 (28) and E2 (black areas; reference 47). Cell-bound antibodies were incubated with FITC-conjugated antibodies before FACS® analysis. The background staining was provided by staining the cells with the conjugated antibodies only (white areas). (B) Immunoblots of lysates of 293T-transfected cells and of pseudo-particles pelleted through 20% sucrose cushions are shown. Expression of E1 and E2 glycoproteins from HCV-1a genotype and of MLV core proteins was revealed in reducing and denaturing conditions with A4 and H52 monoclonal antibodies against E1 (28) and E2 (29) or with an anticapsid (MLV CA) antiserum. VSV-G expressed in control pseudo-particles was detected with the monoclonal antibody P5D4. The positions of the molecular mass markers (kD) are shown. E2 present within the viral pellets migrated slightly slower than the cell-associated forms due to modifications of the associated glycans by Golgi enzymes (not depicted). The presence of VSV-G in viral pellets generated with MLV-G2A assembly-defective core proteins is due to empty vesicles formed by VSV-G itself (48). (C) Immunoblots of lysates of 293T producer cells and of purified pseudo-particles generated with E1 or E2 expressed alone, from two separate expression units, or coexpressed in trans or in cis, from a ΔCE1E2 polyprotein (E1E2).
