Figure 3.
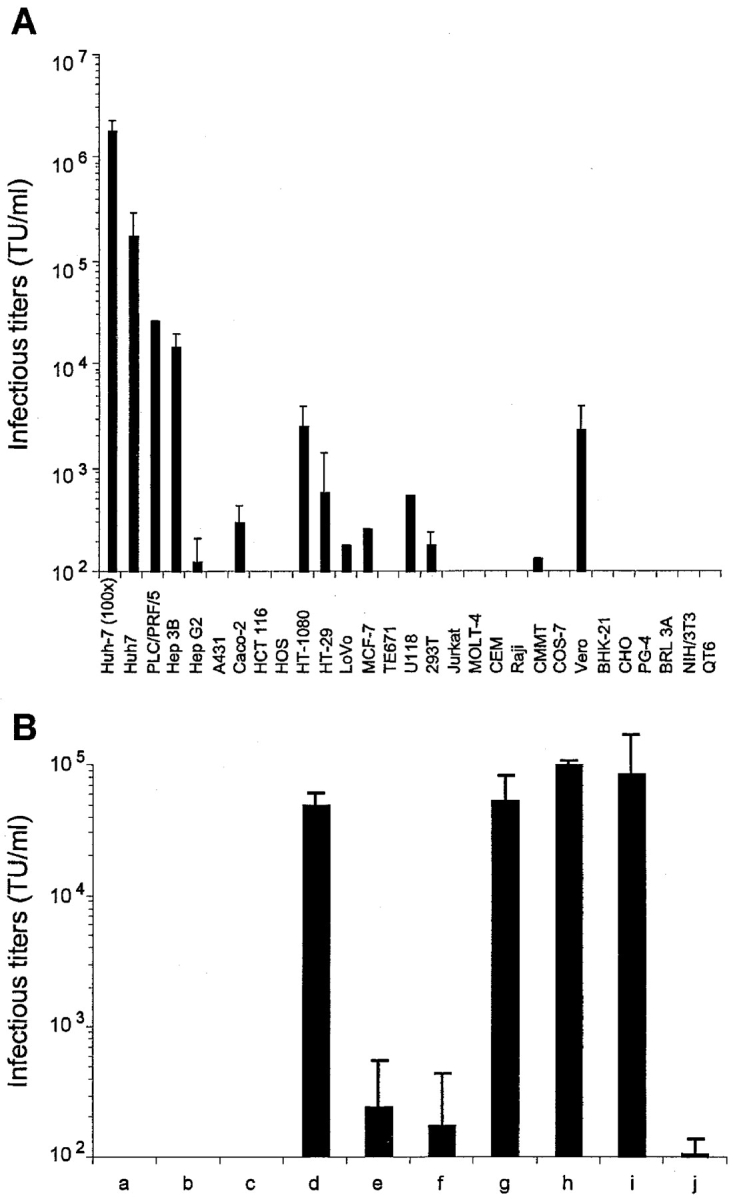
Infectivity of HCV pseudo-particles. (A) The results of experiments performed with different target cell types are displayed as TU per milliliter of supernatant (mean ± SD of up to six experiments) for HCVpp of 1a genotype. The infectivity on Huh-7 cells of HCVpp concentrated 100× by ultracentrifugation is shown. Similar results of infectivity and host-range were obtained for HCVpp of 1b genotype (not depicted). The infectivity of control pseudo-particles generated with VSV-G ranged from 7 × 106 to 2 × 107 TU/ml, depending on the target cell type (not depicted). (B) Infectivity of HCV pseudo-particles generated without E1E2 (a), without retroviral core proteins (b), with MLV-G2A assembly defective core proteins (c), with HIV-1 core proteins (d), with E1 or E2 alone (e or f, respectively), with E1 + E2 expressed in trans from two independents vectors (g), with HCV-1a E1E2 expressed from the same vector in cis (h), or with HCV-1b E1E2 (i). HCVpp were treated with 25 µM AZT (3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine) before and during infection of target cells (j). Infectious titers (TU/ml) were determined on Huh-7 target cells and are displayed as mean ± SD of up to four experiments.
