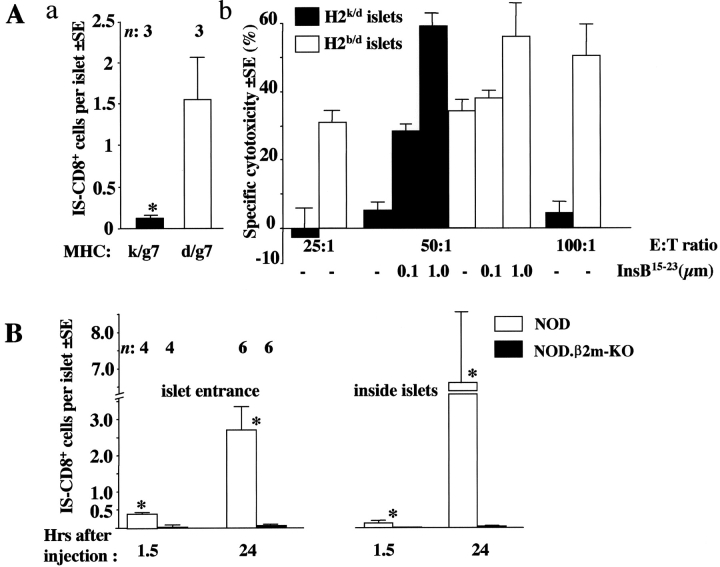
Figure 3.
Lack of specific MHC class I–peptide complexes affects homing of IS-CD8+ cells. (A) In the presence of H2k IS-CD8+ cells fail to migrate into islets (a), or kill islet cells (b). Both properties can be explained by the lack of Kd-InsB15–23 complexes. (a) Labeled IS-CD8+ cells were injected into (C3D2XNOD)F1 mice with either H2k/g7 (filled bar) or H2d/g7 (clear bar) MHC alleles. Morphometric analysis of the pancreata was performed 24 h later. Combined data from two experiments represent mean numbers of IS-CD8+ cells per islet (within white rectangle in Fig. 1)±SE. n, number of mice per group. *, difference vs. H2d/g7 mice is significant by Student's paired t test (P < 0.05). (b) IS-CD8+ cells kill islet cells isolated from H2b/d B6D2 mice, but not the islet cells from H2k/d C3D2 mice. Addition of exogenous InsB15–23 peptide (done at a 50:1 effector-to-target ratio only) restored killing of H2k/d islet cells to the level of killing of H2b/d islets. Data from a representative experiment. (B) Morphometric analysis of pancreata from β2m-deficient, and -sufficient NOD mice for the presence of labeled IS-CD8+ cells at different times after injection. Each cell was ascribed its position as shown in Fig. 1. n, number of mice of each genotype analyzed at each time point. Data show mean numbers of IS-CD8+ cells per islet detected at the indicated location ± SE. *, difference between NOD and NOD.β2m-KO is significant by Student's t test (P < 0.01).