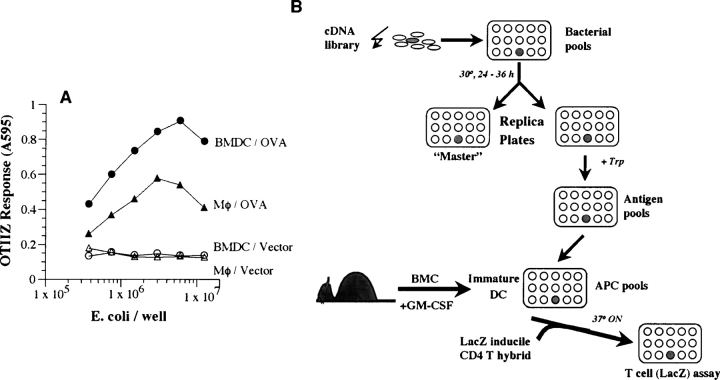
Figure 2.
BMDCs are superior to peritoneal macrophages in the presentation of antigen expressed in E. coli. (A) Varying numbers of E. coli expressing OVA or vector alone were fed to 105 peritoneal macrophages (MΦ) or BMDCs. After a brief incubation, OVA/Ab-specific OTIIZ T cells were added and their lacZ response measured after an overnight incubation. (B) A schematic representation of the strategy for expression cloning CD4 T cell–stimulating antigens. A cDNA library from appropriate donor tissue is prepared in a prokaryotic, tryptophan inducible, expression vector. The transformed E. coli are plated in small pools in a 96-well plate. Expression of the cDNA encoded proteins is obtained in a replica plate of the bacterial cultures by inducing with tryptophan (Trp). The bacterial pools containing the putative antigen are fed to host day 5 BMDCs which phagocytose the bacteria, process and present the antigen/MHC II complexes. The presence of these CD4 T cell ligands is detected by the lacZ response of the CD4 T cell hybrid. The individual bacterial clone is then identified by subcloning the bacteria in the replicate well from the “Master” plate and repeating the screen. See Materials and Methods for details.