Figure 1.
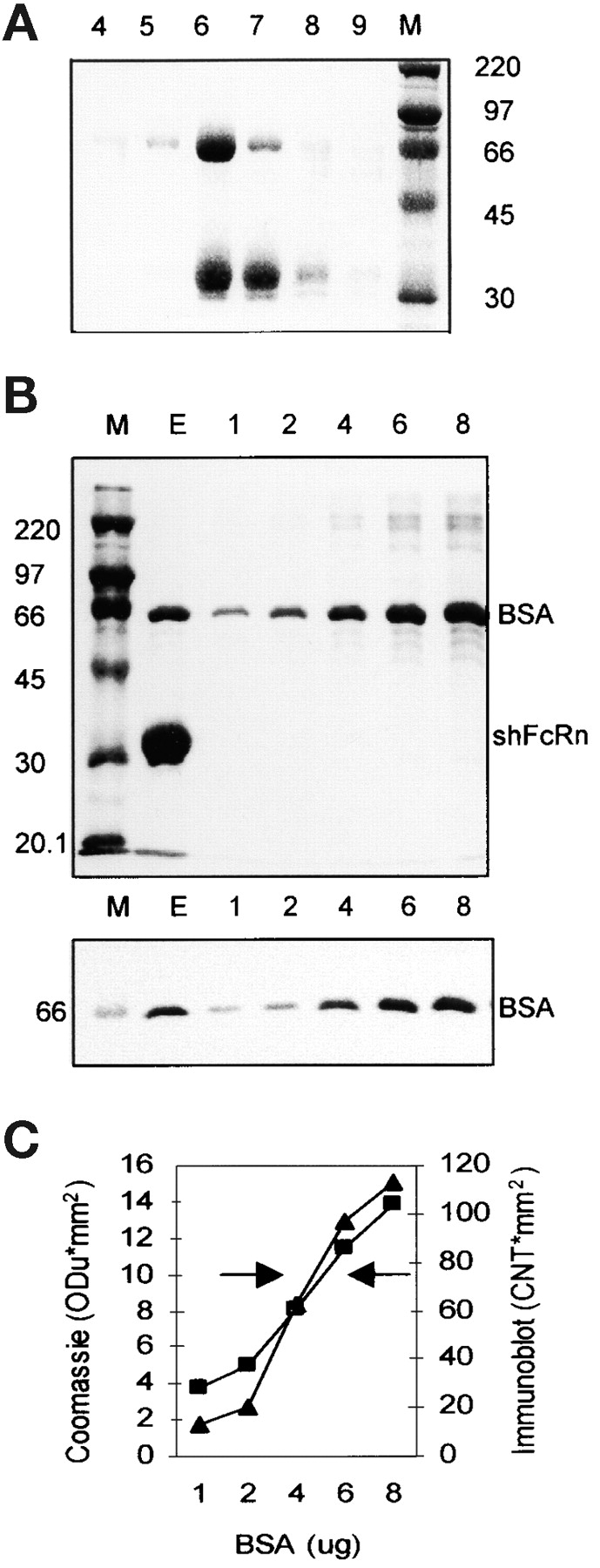
Copurification of BSA and shFcRn by affinity chromatography on Sepharose-hIgG. (A) Culture supernatant from CHO cells secreting recombinant shFcRn was acidified to pH 5.8 and applied to a Sepharose-hIgG chromatography column. Bound shFcRn was eluted at pH 8.1. Six fractions of the elution peak (4–9) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and Coomassie blue staining. The molecular weight markers (M, in kD) allow identification of the α-chain of shFcRn at ∼35kD and another copurifying protein at 67kD. (B) The elution peak (E) from a Sepharose IgG column was analyzed by SDS-PAGE on two identical gels along with molecular weight standards (M) and graded amounts (lanes 1–8; in μg per lane) of BSA. One gel (top) was stained with Coomassie blue and the other (bottom) was immunoblotted with anti-BSA antibody. (C) The band densities in the Coomassie stained gel (▪) and the immunoblot (▴) of B were plotted (on y-axis) against BSA quantity (on x-axis). The left arrow indicates the eluate density on the Coomassie stained gel while the right arrow indicates the density of the eluate on the immunoblot. Three separate experiments have given equivalent results.
