Figure 4.
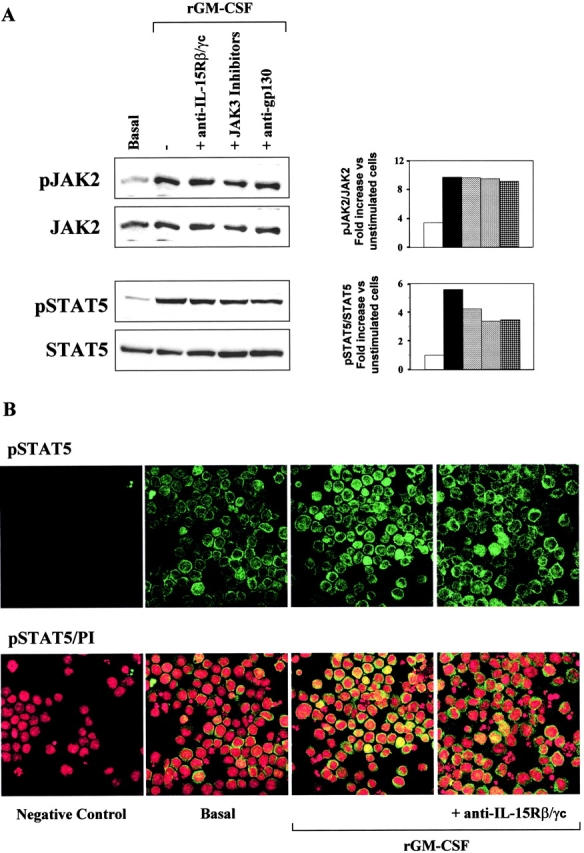
GM-CSF signal transduction: IL-15R/GM-CSFR cross talk in TF1β cells. (A) Analysis of JAK2/STAT5 signal transduction by Western blotting. TF1β cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml rGM-CSF for 15 min at 37°C. Sister cultures were pretreated for 1 h with neutralizing anti–IL-15Rβ/γc mAbs or specific JAK3 inhibitors. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-JAK2 (pJAK2) and anti-phospho-STAT5 (pSTAT5) antibodies. Membranes were then reprobed with antibodies recognizing the native proteins. To correct for possible variations in the amount of protein loaded, values are expressed as pJAK/JAK or pSTAT/STAT ratios. pJAK/JAK and pSTAT/STAT levels were determined by densitometry, including correction for background (NIH Image software). Results are expressed as an increase (e.g., two times) with respect to untreated cells. The data presented are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Analysis of pSTAT5 nuclear localization by confocal microscopy. TF1β cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml rGM-CSF for 15 min at 37°C. Sister cultures were pretreated for 1 h with neutralizing anti-IL-15Rβ/γc mAbs. Control (basal) and treated cultures were analyzed by confocal microscopy for pSTAT5 distribution in the cell, focusing particularly on whether this protein was present in the nucleus. Propidium iodide stains nuclei red whereas pSTAT5 is stained green. Yellow staining indicates the presence of pSTAT5 in the nucleus.
