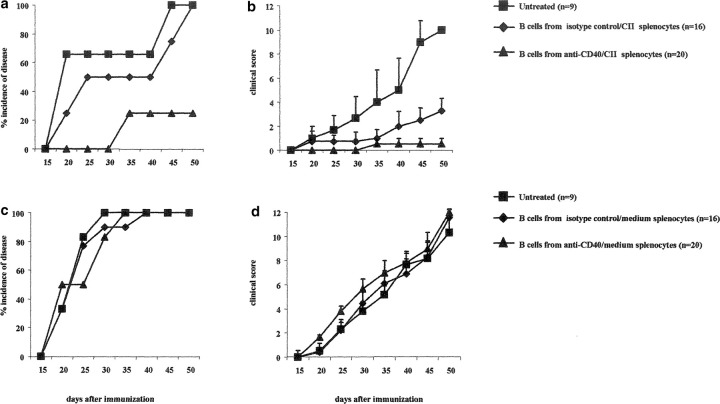
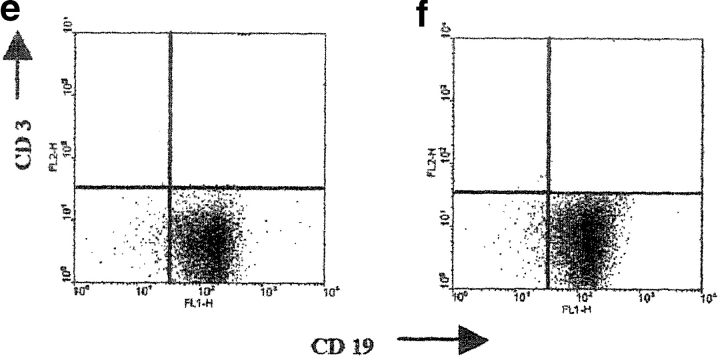
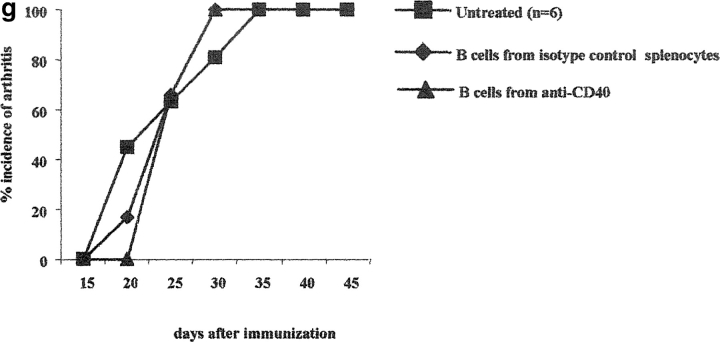
Figure 4.
Transfer of B cells isolated from anti-CD40 activated splenocytes prevents chronic arthritis development. (a–c) DBA/1-TcR-β-Tg splenocytes were stimulated in vitro for 48 h with isotype control/CII; isotype control alone or with anti-CD40/CII or anti-CD40 alone. B cells were enriched by negative selection, using an anti-CD43 magnetic beads conjugated antibody, and 5 × 105 B cells were transferred intraperitoneally, at the time of CII/CFA immunization, to syngeneic mice. Percentage of mice with arthritis. Mice groups were compared by statistical analysis using the Fisher exact test. (b–d) Severity of disease. The data represent the mean of (n) mice ± SE and they are representative of five experiments. Groups of mice were compared by statistical analysis using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. The purity of B cells, isolated from (e) control or (f) anti-CD40–treated splenocytes, was checked before transfer, by staining the negative fraction with FITC-conjugated anti-CD19 and PE-conjugated anti-CD3 mAbs. (c and d) DBA/1-TcR-β-Tg splenocytes were stimulated in vitro for 48 h with isotype control or with anti-CD40 alone. B cells were enriched by negative selection, using an anti-CD43 magnetic beads conjugated antibody, and 5 × 105 B cells were transferred intraperitoneally, at the time of CII/CFA immunization, to syngeneic mice. Percentage of mice with arthritis. (g) B cells were enriched by negative selection, using an anti-CD43 magnetic beads conjugated antibody, from DBA/1-TcR-β-Tg arthritogenic splenocytes. Purified B cells were stimulated in vitro for 48 h with isotype control/CII; or with anti-CD40/CII. 5 × 106 B cells were transferred intraperitoneally, at the time of CII/CFA immunization, to syngeneic mice. A group of mice was left untreated. Percentage of mice with arthritis. Data are representative of four experiments.