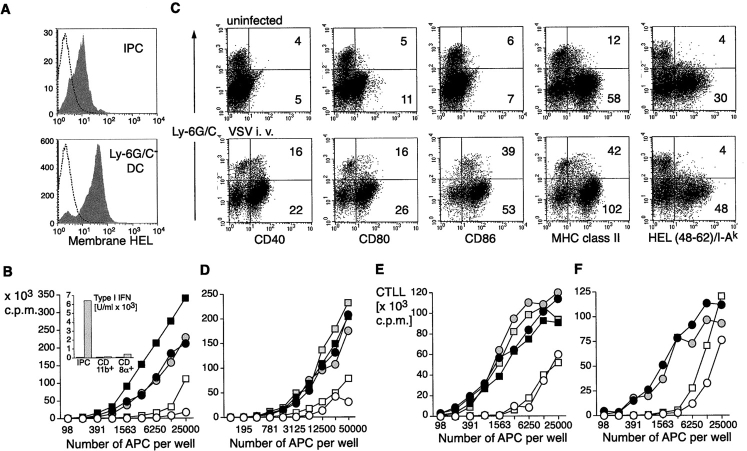
Figure 1.
HEL expression and antigen presentation to HEL-specific naive CD4 T cells and 3A9 T cell hybridoma by primary mHEL-transgenic DCs and IPCs. (A) IPCs and Ly-6G/C− DCs from the mHEL mouse were stained with an antibody specific for HEL to measure antigen expression at the cell surface (gray histograms). Open histograms indicate staining with control antibody. (B) Proliferative response of HEL-specific naive 3A9 CD4 T cells (104) cultured with graded numbers of purified IPCs (open symbols), CD11b+(black filled symbols), and CD8α+ (gray filled symbols) DCs derived from mHEL mice. IPCs and DCs were untreated (circles) or treated (squares) in vitro for 12 h with PR8 (1 MOI) before addition of T cells. Supernatants were then collected and type I IFN production was measured (insert to B). Proliferation was measured after 72 h. (C) Expression of costimulatory molecules, MHC class II and HEL48–62/IAk specific complexes in IPCs and DCs derived from mHEL-mice. Mice were either uninfected or challenged with VSV for 12 h. MFI for IPCs and Ly-6G/C− DCs are indicated. (D) Proliferation of 3A9 naive CD4 T cells cocultured with graded numbers of IPCs or DCs purified ex vivo from mHEL mice uninfected or infected with VSV (intravenous, 2 × 108 PFU) 12 h before. (E and F) HEL-specific 3A9 cell hybridoma T cells (105) were cocultured with graded numbers of IPCs and DCs sorted from mHEL mice and stimulated in vitro with influenza virus PR8 (E) or activated in vivo by VSV infection (F). Supernatants were collected after 48 h and the IL-2 produced upon activation was measured as proliferation of CTLL cells after 20 h.