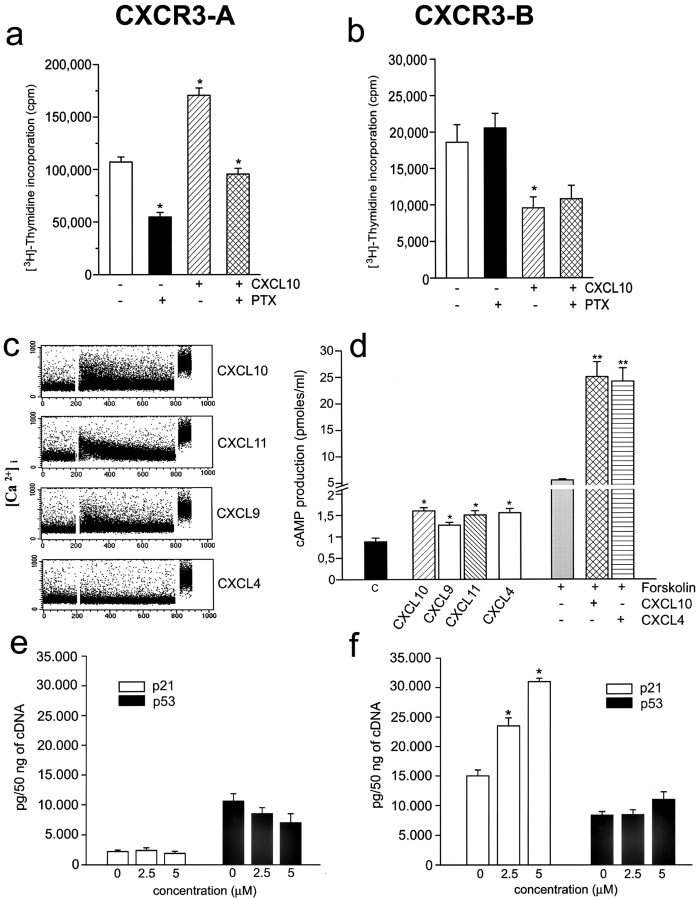
Figure 4.
Activation of distinct signal transduction pathways in CXCR3-A and CXCR3-B transfectants. (a) Increased proliferative activity in CXCR3-A transfectants is strongly reduced by PTX both in basal conditions and after treatment with 500 nM CXCL10. (b) PTX has no effect on the proliferation of CXCR3-B transfectants both in basal conditions and after treatment with 4 μM CXCL10. Cells were incubated for 60 h with 1 μg/ml PTX and thymidine incorporation was assessed in the last 12 h. Columns represent mean values (±SD) of three separate experiments. *, P < 0.05. (c) Induction by CXCL10, CXCL9, and CXCL11 (1 μM), but not by CXCL4 (1 μM), of Ca++ mobilization in CXCR3-A transfectants. Results are from one representative of four experiments. (d) Effect of CXCL10, CXCL9, CXCL11, and CXCL4 (2 μM) on basal cAMP production and of CXCL10 and CXCL4 (2 μM) on forskolin (1 μM)-stimulated cAMP production in CXCR3-B transfectants. Columns represent mean values (±SD) of six separate experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001. (e) Absence of p21Cip1/Waf1 and p53 regulation by CXCL4 in CXCR3-A transfectants as assessed by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. (f) Up-regulation in CXCR3-B transfectants of p21Cip1/Waf1, but not of p53, mRNA levels by increasing concentrations of CXCL4 as assessed by real-time quantitative RT-PCR.