Figure 6.
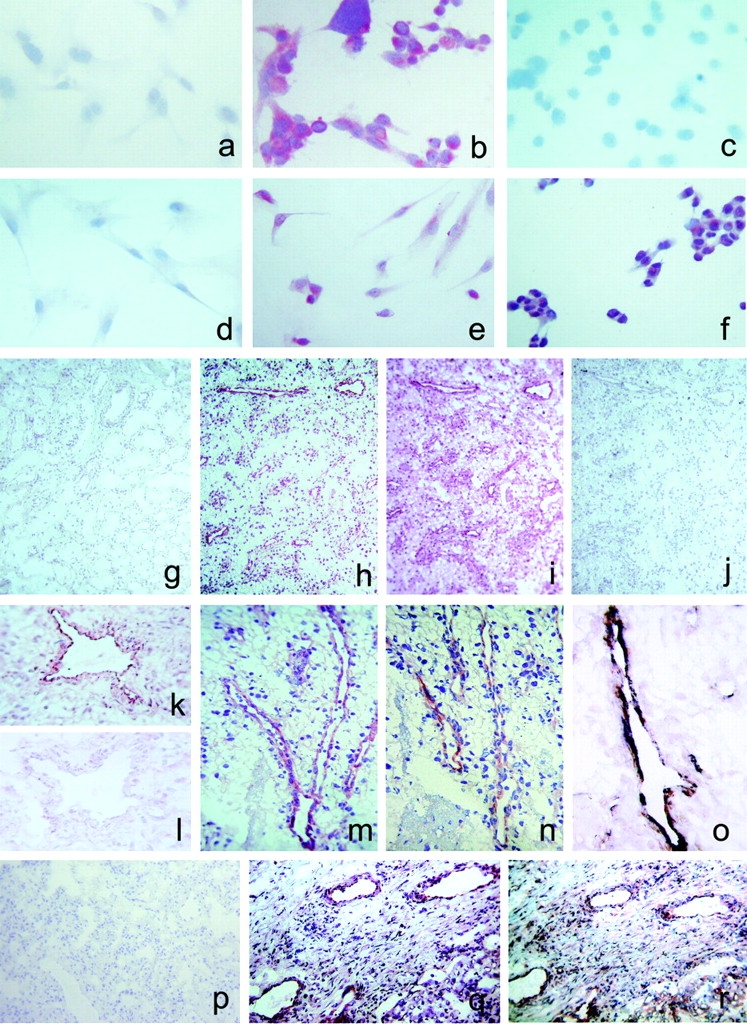
Detection of CXCR3-B protein expression by different types of cell cultures and by endothelial cells of human neoplastic tissues by CXCR3-B–specific mAbs. (a) Absence of reactivity in mock transfectants stained with an anti-CXCR3-B mAb. ×100. (b) Intense staining of CXCR3-B transfectants with an anti–CXCR3-B mAb. ×100. (c) Absence of reactivity in CXCR3-A transfectants stained with an anti–CXCR3-B mAb. ×100. (d) Absence of reactivity in primary cultures of HMC stained with an anti–CXCR3-B mAb. ×100. (e) Positive staining of primary cultures of HMVEC as well as the ACHN cell line (f) with an anti–CXCR3-B mAb. ×100. (g) Absence of reactivity in normal human renal tissue stained with PL1 anti–CXCR3-B mAb. ×10. (h) Staining with the same mAb of endothelial cells in a specimen of renal cell carcinoma. (i) Staining of both endothelial and tumor cells with the anti-CXCR3 mAb 49801.111 tested in an adjacent section. (j) Absence of reactivity in an adjacent section stained with an isotype-matched control mAb. (k and l) Reactivity of endothelial cells from the same renal carcinoma specimen before and after adsorption of PL1 mAb with the peptide used for mouse immunization. (m) Reactivity with PL1 mAb of endothelial cells from a group of vessels in a renal cell carcinoma specimen as detected at a higher power magnification. ×250. (n) Staining of an adjacent section with PL2 anti–CXCR3-B mAb. (o) Double label immunohistochemistry for CXCR3-B (red) and vWf (blue-gray), showing costaining (brown). (p) Absence of CXCR3-B reactivity in normal human lung tissue stained with PL1 anti–CXCR3-B mAb. (q) Staining with the same mAb of endothelial cells in a specimen of NSCLC. (r) Staining of both endothelial cells and other cell types with the anti-CXCR3 mAb 49801.111 in an adjacent section.
