Figure 4.
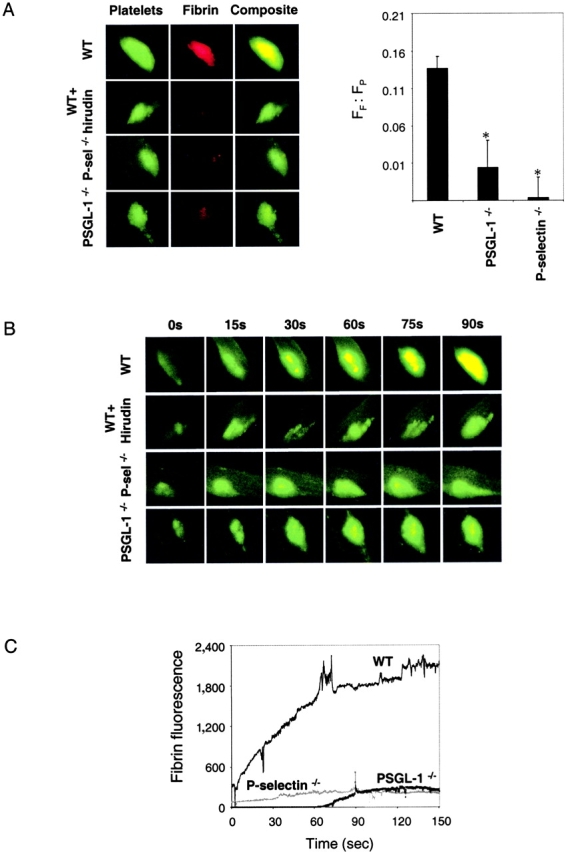
Fibrin deposition in the developing thrombus. (A) Left: Alexa 660–conjugated anti–mouse fibrin antibody and rat anti–mouse CD41 detected with Alexa 488–conjugated chicken anti–rat IgG were used to detect fibrin (red) and platelets (green). Overlap of the platelet and fibrin images is shown as a composite (yellow). When used, hirudin (1 U/g body weight) was infused immediately before initial thrombus formation. Fibrin and platelets were observed in thrombi formed 60 s after vessel injury. Images are representative of 10 thrombi formed in 6 arterioles in 3 mice of each genotype. Right: the ratio of the integrated fibrin fluorescence (FF) to the integrated platelet fluorescence (FP) in thrombi generated in wild-type mice, PSGL-1 null mice, and P-selectin null mice is shown (black) based upon multiple independent experiments. The fluorescence background in the absence of fibrin was determined in wild-type mice treated with hirudin. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean whereas * indicates statistical significance. (B) Images of the developing thrombus from 0–90 s. Platelets (green), fibrin (red), and platelet/fibrin composite (yellow). (C) Time course of fibrin formation in the developing thrombi of wild-type and genetically altered mice. Each curve represents the raw digital data of a single representative experiment. WT, wild-type mouse; PSGL−/−, PSGL-1 null mouse; P-selectin−/−, P-selectin null mouse.
