Figure 6.
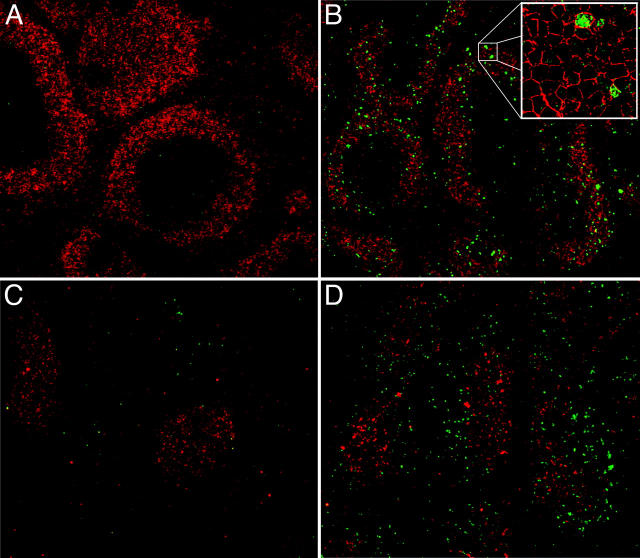
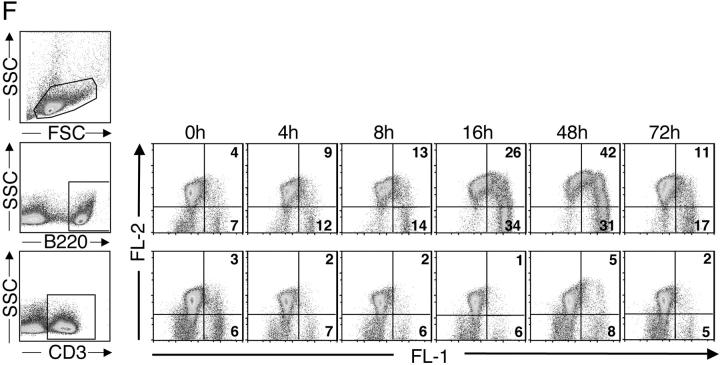
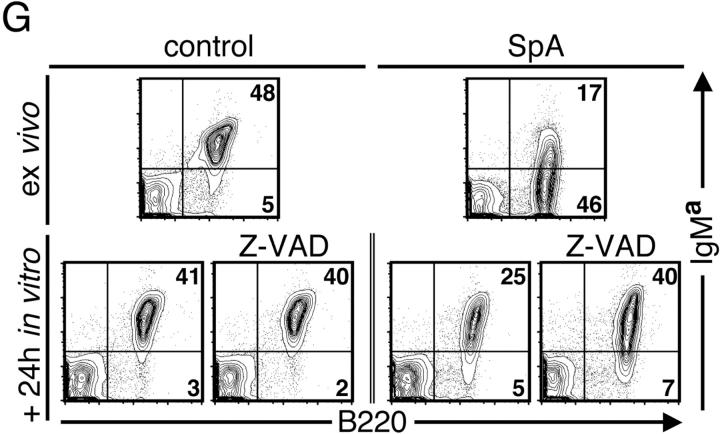
Apoptotic pathways induced in VH-susceptible T15i+/+ B cells during the degradation phase that follows in vivo treatment with SpA. At time of harvest (48 h ex vivo), there is evidence of increased DNA fragmentation detected by the TUNEL assay (green) in B cells from T15i+/+ mice that received SpA (B and D) compared with control (A and C). A and B were stained with B220 and C and D were stained with CD3 (red). (E) After in vivo treatment of Fas ligand–deficient (gld) or congenic (C57BL/6) mice that received CFSE-labeled T15i+/+ splenocytes, at 48 h the intracellular levels of activated caspase 3 are greatly enriched in susceptible B cells (i.e., B220+) from SpA-treated mice (bold line) compared with those receiving control treatment (shaded). By contrast, differences are not seen in non-B cells (i.e., B220−). Panels depict data gated on CFSE+ events (refer to methods in Table I). (F) Results are depicted for cytometric assays of ΔΨm. Splenic B cells are identified by gating on B220+ cells or T cells by CD3+ staining. Herein, the dissipation of ΔΨm is identified based on increased shift in FL-1 and lower levels of staining with the specific fluorescent dye detected in FL-2. Results of splenic lymphocytes are depicted for mice that received SpA treatments at 0, 4, 8, 16, 48, and 72 h before they were killed. (G) The caspase pathway contributes to SpA-induced apoptotic B cell death. After 16 h of in vivo exposure, splenocytes from control or SpA-treated T15i+/+ mice were placed in culture with or without a general caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD. After in vitro culture, although the VH-susceptible B cells from SpA-treated mice undergo accelerated apoptotic death after an additional 24 h in culture, compared with those from control (OVA) mice, the addition of the caspase inhibitor enhances the survival of SpA-exposed T15i-expressing splenic B cells. The data are representative of three or more experiments.