Figure 4.
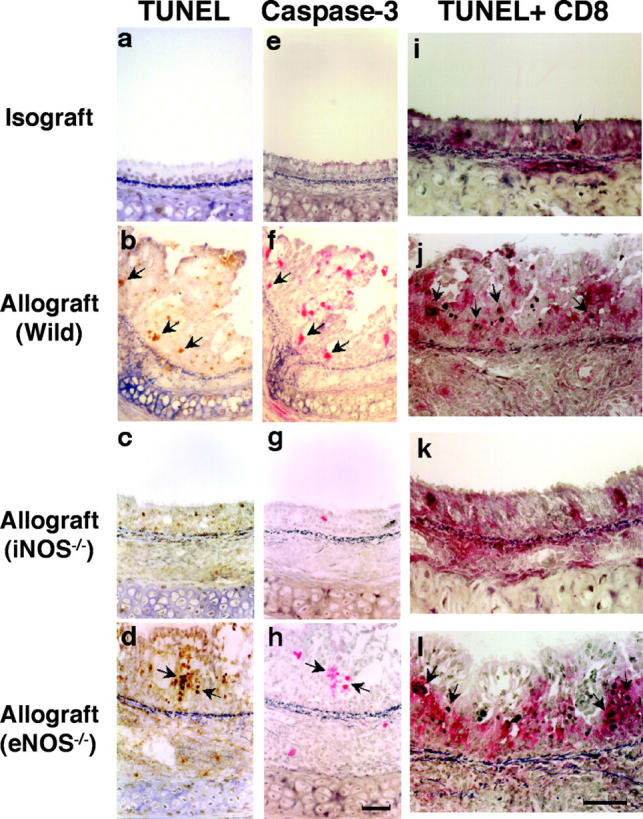
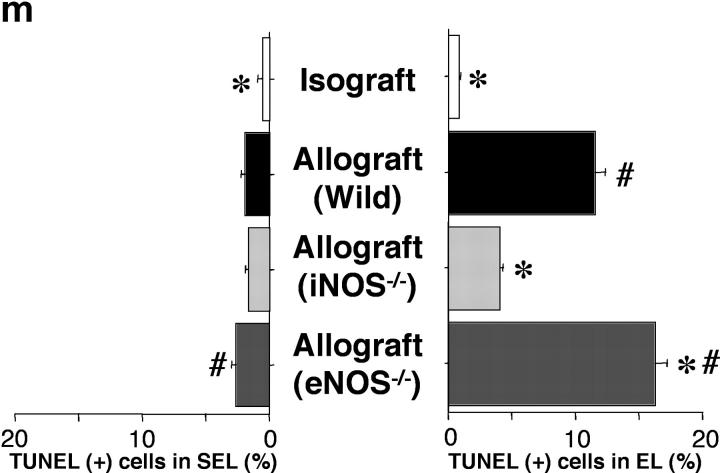
Apoptotic cells were detected using the in situ TUNEL labeling method (a–d; arrows) and further corroborated immunohistochemically by colocalizing caspase-3 expression in the same cells in adjacent sections (e–h; arrows). Double staining for apoptotic CD8+ T lymphocytes (i–l; arrows) is detected by black nuclear labeling for apoptosis and red cytoplasmic staining for CD8. Apoptosis of CD8+ T lymphocytes (arrows) was most abundant in the EL of allografts placed in WT and eNOS−/− recipients. The graph (m) shows quantitative T lymphocyte apoptotic activity in both the EL and SEL of the graft. Apoptosis of T lymphocytes was reduced by recipient iNOS deficiency. *, P < 0.05 versus allografts from WT recipients; #, P < 0.05 versus allografts from iNOS−/− recipients; bar, 50 μm.