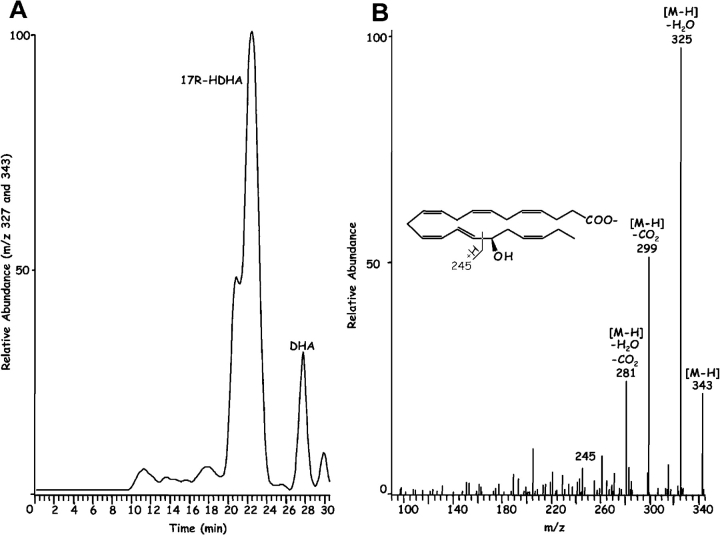
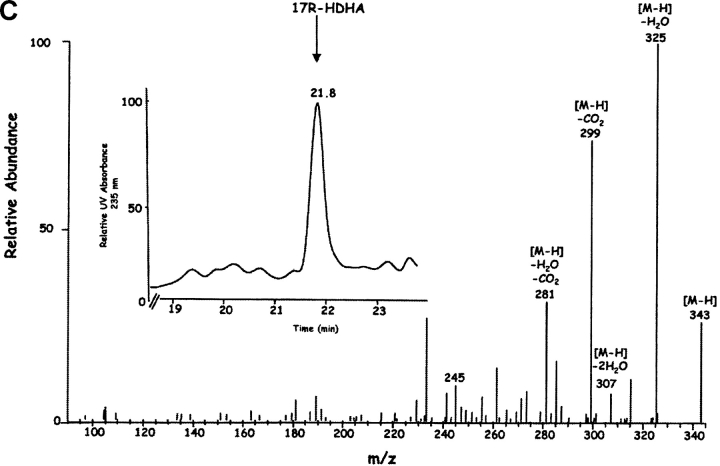
Figure 3.
Endogenous 17R-HDHA from brain and human microglial cells treated with aspirin. (A) LC-MS-MS chromatogram obtained from brain for relative abundance at m/z 327 for DHA and m/z 343 for the monohydroxy product. (B) MS-MS spectrum of brain 17R-HDHA (m/z 343). Murine brain samples were incubated with ASA (45 min, 37°C). Results are representative of n = 6 mice treated with ASA versus five mice without ASA. (C) Human microglial cells (HMG) treated with ASA; MS-MS spectrum of HMG 17R-HDHA. 10 × 106 cells were exposed to 50 ng/ml TNF-α and incubated (24 h, 37°C). Cells were treated with ASA (500 μM, 30 min, 37°C) followed by addition of ionophore A23187 (5 μM, 25–30 min). Incubations were stopped with MeOH, extracted and analyzed by tandem UV, LC-MS-MS (Fig. 3 inset shows UV-chromatogram plotted at 235 nm absorbance) (n = 4, d = 20). Both 17R-HDHA and DHA were identified on the basis of individual retention times, parent ions, and daughter ions obtained.