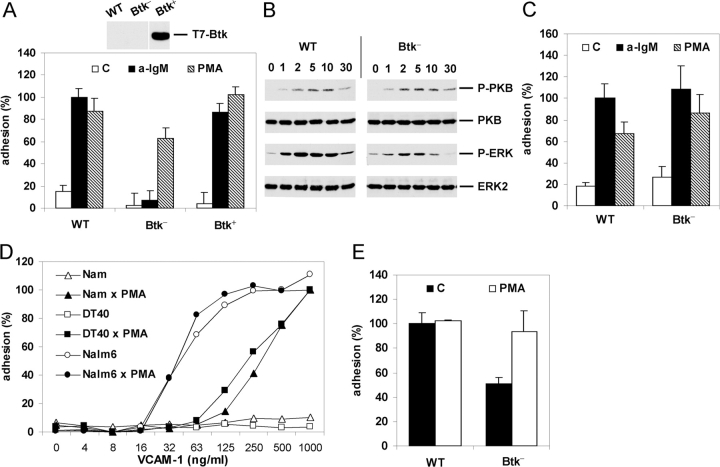
Figure 3.
Btk is required for BCR-controlled adhesion. (A) WT, Btk-deficient (Btk−), or Btk-deficient DT40 cells reconstituted with Btk (Btk+) were not stimulated (C) or stimulated with anti-IgM (a-IgM) or PMA and plated on a surface coated with VCAM-1. The inset shows expression of Btk in the Btk-reconstituted DT40 cell-line as detected by immunoblotting with anti-T7. (B) Activation of PKB and ERK in WT or Btk-deficient (Btk−) DT40 cells after stimulation with anti-IgM for the indicated period of time (min). The blots are probed as in Fig. 2 B. (C) B cells from WT or Btk-deficient (Btk−) mice were not stimulated (C) or stimulated with anti-IgM (a-IgM) or PMA and plated for 15 min on a surface coated with 0.3 μg/ml VCAM-1. The experiment shown is representative for two independent experiments. (D) Nalm6 (circles), DT40 (squares), or Namalwa (triangles) cells were not stimulated (open symbols) or stimulated with PMA (closed symbols) and plated for 20 min on a surface coated with different concentrations of VCAM-1. The adhesion was normalized to 100% for the PMA-stimulated cells plated on 1 μg/ml VCAM-1. The experiment shown is representative for two independent experiments. (E) Pre-B cells from WT or Btk-deficient (Btk−) mice were not stimulated (C) or stimulated with PMA and plated for 15 min on a surface coated with 0.3 μg/ml VCAM-1. The adhesion was normalized to 100% for the unstimulated WT preB cells. The bars represent the means ±SD of 2 WT and 2 Btk-deficient mice, each assayed in triplicate. In a total of three independent experiments (6 WT and 6 Btk-deficient mice), the basal adhesion of the Btk-deficient mice was 54% ± 10% in comparison to WT preB cells.