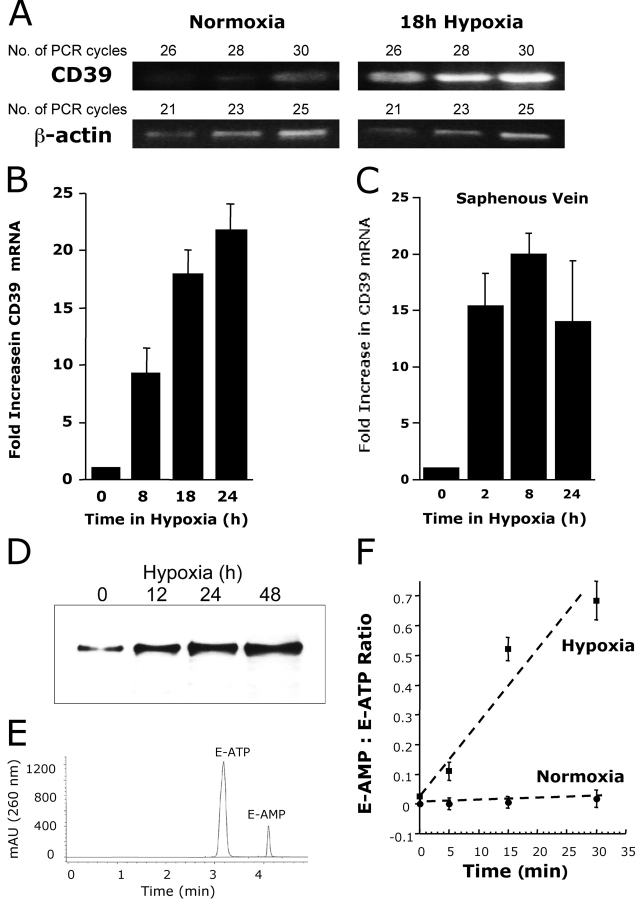
Figure 3.
Induction of functional CD39 is by hypoxia. (A) Confluent HMEC-1 monolayers were exposed to normoxia (pO2 147 torr, 18 h) or hypoxia (pO2 20 torr, 18 h). Total RNA was isolated, and CD39 mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR using semiquantitative analysis (increasing cycle numbers, as indicated). As shown, β-actin transcript was determined in parallel and used as a control. (B) Real-time PCR was employed to confirm hypoxia inducibility of CD39 in cultured endothelial cells (HMEC-1). Data were calculated relative to internal housekeeping gene (β-actin) and are expressed as fold increase over normoxia ± SD at each indicated time. Results are derived from three experiments in each condition. (C) Human saphenous vein was obtained from patients undergoing aorto-coronary bypass surgery and exposed ex vivo to ambient normoxia (pO2 147 torr, 24 h) or hypoxia (pO2 20 torr for 2, 8, or 24 h). After total RNA isolation, real-time PCR was performed to investigate CD39 inducibility by hypoxia. Data were calculated relative to internal control (β-actin) and are expressed as fold increase over normoxia ± SD at each indicated time. Results are derived from three experiments in each condition. (D) Increase in surface CD39 surface protein with hypoxic exposure. Confluent HMEC-1 monolayers were exposed to indicated periods of hypoxia, monolayers were washed, surface proteins were biotinylated, and cells were lysed. CD39 was immunoprecipitated with mAb directed against human CD39. Immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and resultant Western blots were probed with avidin-peroxidase. A representative experiment of three is shown. (E) Validation etheno-ATP (E-ATP) and etheno-AMP (E-AMP) resolution by HPLC. Shown is a representative tracing indicating resolution of definitive peaks at UV 260 nm. (F) Functional increase in CD39 surface activity by hypoxia. Endothelial monolayers were exposed to 48 h hypoxia or normoxia, washed, and surface CD39 activity was determined by HPLC analysis of E-ATP conversion to E-AMP in the presence of the CD73-inhibitor αβ-methylene-ADP (10 μM, to prevent further metabolism of E-AMP to E-adenosine). Data are derived from five to seven monolayers in each condition, and results are expressed as E-AMP: E-ATP ratio ± SD.