Figure 7.
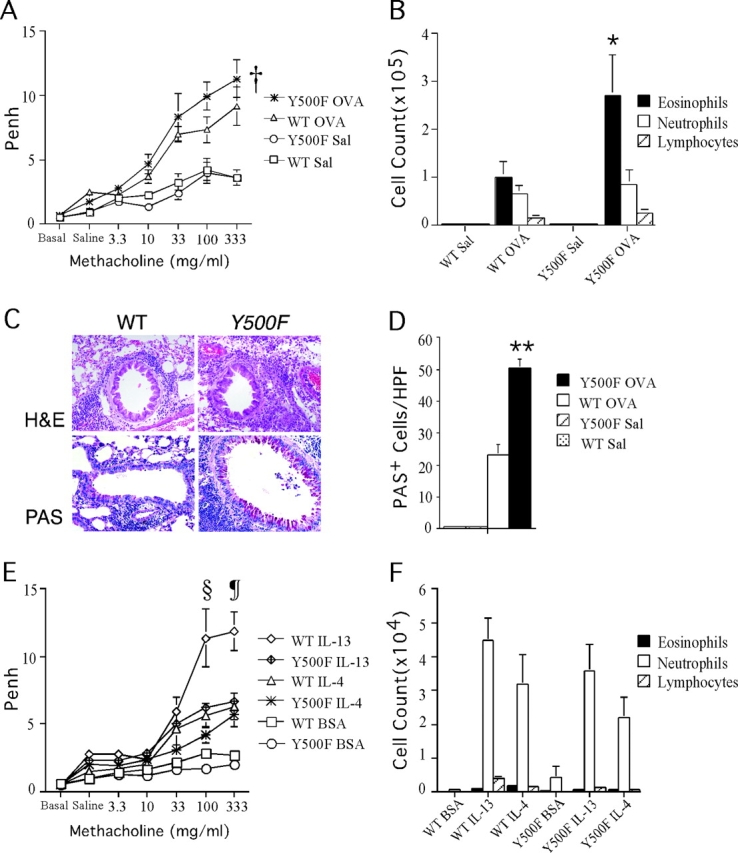
The Y500F mutation enhances AHR, tissue eosinophilia, and goblet cell metaplasia in an antigen-induced model of allergic airway inflammation. (A) AHR to aerosolized methacholine in WT and Y500F mutant mice (n = 5–6/group) immunized with OVA/alum or sham immunized with saline/alum mix and then subsequently challenged with aerosolized OVA. AHR was assessed by enhanced respiratory pause (Penh). Results are means ± SE; †P = 0.03 (versus IL-4Rα Y500F OVA). (B) Differential count of inflammatory cells found in BAL fluid of mice tested in A. *P = 0.04 (versus IL-4Rα Y500F OVA). (C) Lung histology of WT and IL-4Rα Y500F mutant mice sensitized and challenged with OVA. H&E, hematoxylin-eosin; PAS, periodic acid-schiff reagent. (D) The number of mucin-positive cells in the bronchi of OVA-treated WT and Y500F animals. PAS-stained lung sections were scored for the number of mucin-secreting cells per high power field (HPF, 400×) in central medium-sized bronchi. Three representative fields were counted for each of three mice in each group. **P < 0.0001 (versus IL-4Rα Y500F OVA). (E) AHR to aerosolized methacholine in WT and Y500F mutant mice (n = 14–15 mice/group) tested after intranasal instillation of IL-4, IL-13, or BSA at 5 μg each. (F) Differential count of inflammatory cells found in BAL fluid of mice tested in E. §P = 0.03; ¶P = 0.016 versus IL-4Rα Y500F IL-13 at 100 and 333 mg methacholine/ml, respectively.
