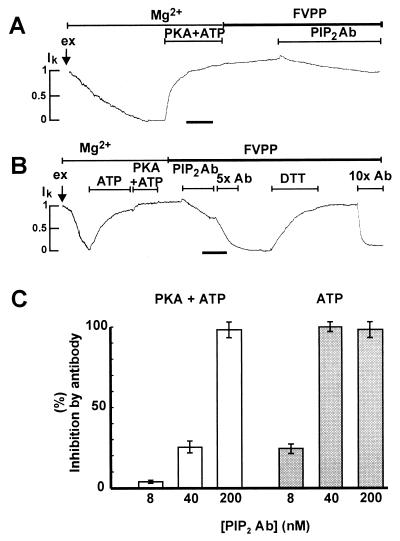
Figure 2.
PKA activates run-down channels to the same maximal restorable level as ATP and reduces the sensitivity of the channels to anti-PIP2 antibody. Membrane patches were excised and allowed to run down in Mg2+ solution as in Fig. 1. The horizontal time bar is 120 sec. (A) PKA catalytic subunit (100 units/ml) + Mg-ATP (0.5 mM) activated the channels to the same maximal level of on-cell current as ATP (see Fig. 1 A and B). Anti-PIP2 antibodies (40 nM) inhibited the channel only partially in 5 min. (B) PKA + ATP was not further stimulatory to the channels that were maximally activated by ATP. Increasing concentrations of anti-PIP2 antibodies (5× Ab, 200 nM, and 10× Ab, 400 nM) inhibited the channels faster. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of the channels by anti-PIP2 antibody. Channels were allowed to run down in Mg2+ solutions and were reactivated by ATP (shaded bars) or PKA + ATP (open bars). Thereafter, anti-PIP2 antibodies (8, 40, or 200 nM) were applied to the channels in FVPP solutions. Mean ± SEM, n = 3–16 for each group.