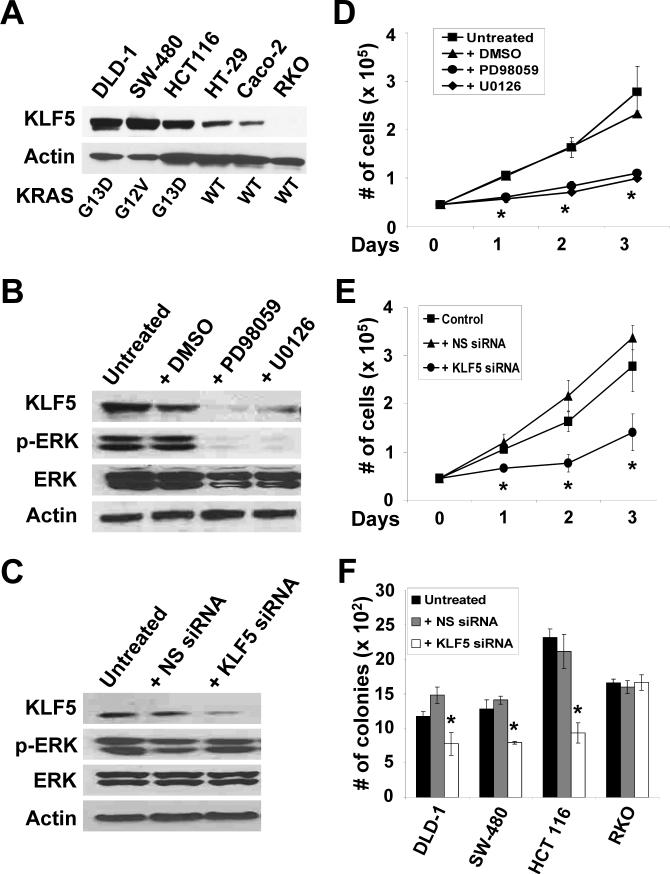
Figure 5. Human colorectal cancer cell lines containing oncogenic KRAS have high KLF5 levels.
(A) Six human colorectal cancer cell lines were cultured and cell lysates extracted when sub-confluent. Proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using KLF5 and β-actin antibodies. KRAS codons 12, 13 and 61 were sequenced and oncogenic mutations, if present, were noted. WT is wild type. (B) DLD-1 cells were treated with 50 μM MEK inhibitors, PD98059 and U0126, or DMSO for 24 h or left untreated. Proteins were extracted and analyzed by Western blotting for KLF5, p-ERK, ERK and β-actin. (C) DLD-1 cells were either untreated or transfected with KLF5-specific siRNA or non-specific (NS) siRNA and cell lysates prepared 24 h after transfection. Western blot analysis was performed for KLF5, p-ERK, ERK and β-actin. (D) Cell proliferation was measured in DLD-1 cells treated with MEK inhibitors, DMSO or left untreated for up to three days. N = 6; * p < 0.05, comparing MEK inhibitor-treated and DMSO-treated cells. (E) Cell proliferation was determined in DLD-1 cells transfected with KLF5-specific or NS siRNA for up to three days post transfection. N = 6; * p < 0.05, comparing KLF5 siRNA and NS siRNA-transfected cells. (F) Anchorage-independent growth was examined in soft agar for DLD-1, SW-480, HCT 116 and RKO cells. Untransfected, KLF5 siRNA or NS siRNA-transfected cells were evaluated 21 days post-treatment for colony number. N = 6; * p <0.01.