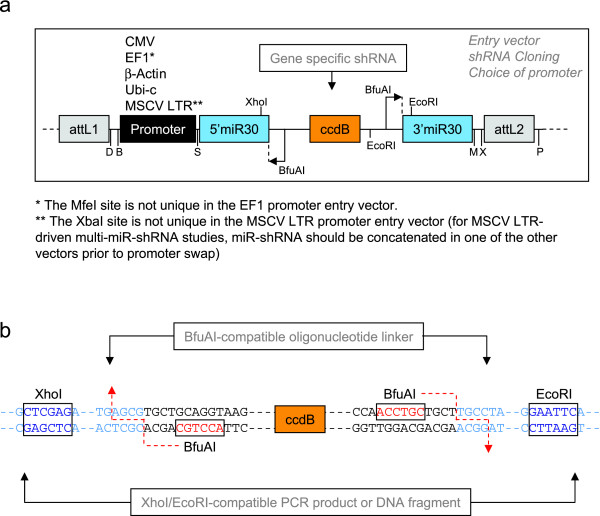
Figure 2.
Entry vector design and miR-shRNA cloning strategy. (A) Schematic showing the architecture of entry vectors for miR-shRNA cloning. Vectors were created with five different promoter options; CMV, EF1, β-actin, Ubiquitin-c and MSCV LTR. Single letters denote the following restriction enzyme sites: D; DpaI, B; BamHI, S; SpeI, M; MfeI, X; XbaI, P; PstI. These sites are unique apart from the exceptions noted below the figure. The ccdB is a counterselection gene toxic to most E.coli strains, which reduces parent vector background when cloning shRNAs. (B) Sequence details around the shRNA cloning sites demonstrate alternative methods of shRNA insertion into an entry vector. For shRNAs cloned as BfuAI site-compatible linkers (see methods), shRNA sequence is introduced at the junctions of the 5' and 3' miR30 sequence (light blue). For shRNAs subcloned from commercially available whole genome libraries [2, 7], fragments can be subcloned to the XhoI/EcoRI sites (dark blue) within the 5' and 3' miR30 sequence.