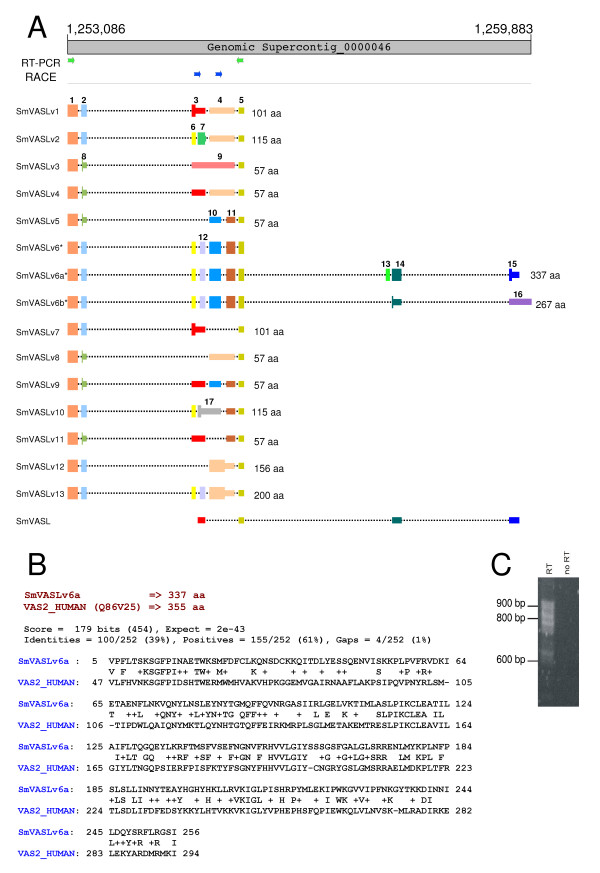
Figure 4.
S. mansoni Vasohibin-like (SmVASL) isoforms. A: Schematic representation of SmVASL transcripts aligned to the S. mansoni genomic sequence. The thick gray bar at the top represents the genomic sequence of Supercontig_0000046. Coding sequences, UTRs and introns are represented by thick, thin and dashed lines, respectively. We have colored and numbered the different exons consecutively in an arbitrary way, in the order that each new exon splicing form appears in Figure 4A. Primers that were used for the RT-PCR amplification and RACE experiments of SmVASL alternatively spliced forms are represented by green and blue arrows, respectively. Deduced protein-coding ORFs of SmVASL message are represented by thick colored lines, and the lengths of the deduced encoded proteins are displayed at the right side of each splice variant. The asterisks next to SmVASLv6, SmVASLv6a and SmVASLv6b indicate that the latter two are the result of a 3'-RACE-PCR experiment (3'-RACE primers represented by blue arrows); B: Local alignment (BLAST) showing the conserved region of SmVASLv6a and human vasohibin 2; C: Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products from a reaction performed with primers indicated in panel A with green arrows. RT indicates that cDNA was synthesized by Reverse Transcriptase with poly-dT priming using RNA as template, and PCR was subsequently performed. No RT indicates a negative control where PCR was performed with an RNA sample incubated with poly-dT but no reverse transcriptase, to control for the absence of genomic DNA contamination.