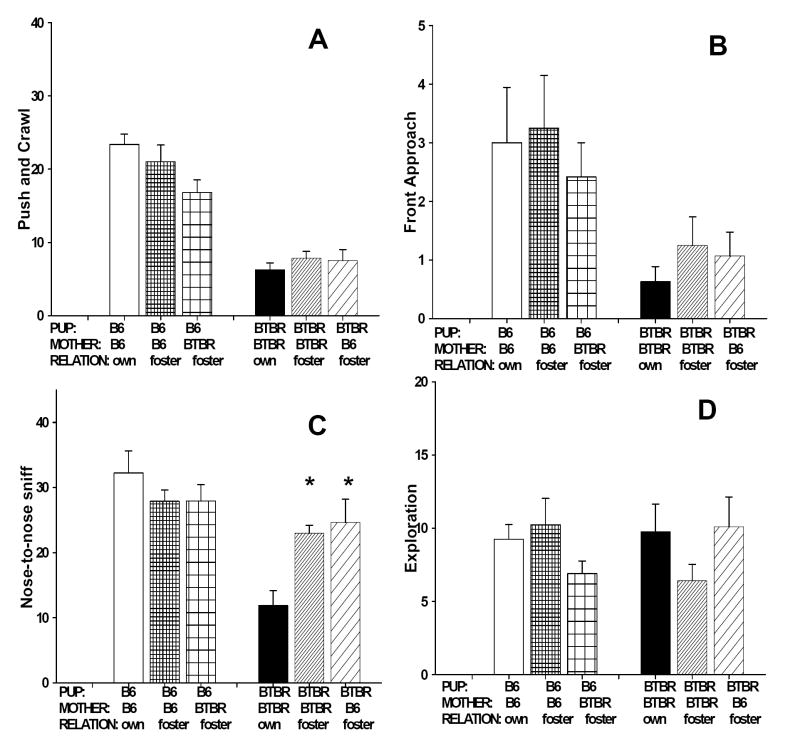
Figure 2.
Juvenile play test. No significant maternal strain or significant strain x maternal environment interaction was detected for push/crawl, front approach, and exploration. Significant pup strain differences were found for push/crawl, front approach, nose sniff, but not exploration. (A) B6 pups showed higher levels of push/crawl than BTBR pups (B) B6 pups showed higher levels of front approach than BTBR pups. (C) B6 pups showed higher levels of nose sniff than B6 pups raised in any maternal environment. A significant strain x maternal environment interaction was detected for nose sniff. BTBR pups raised by foster BTBR mother or B6 mothers showed more nose sniff as compared to BTBR raised by their own mothers. (D) All groups showed similar levels of exploration, indicating no strain difference or maternal effect on locomotor activity. *, p<.05 as compared to BTBR pups raised by their own mothers. Data are shown as mean + standard error of the mean in Figures 2-4.