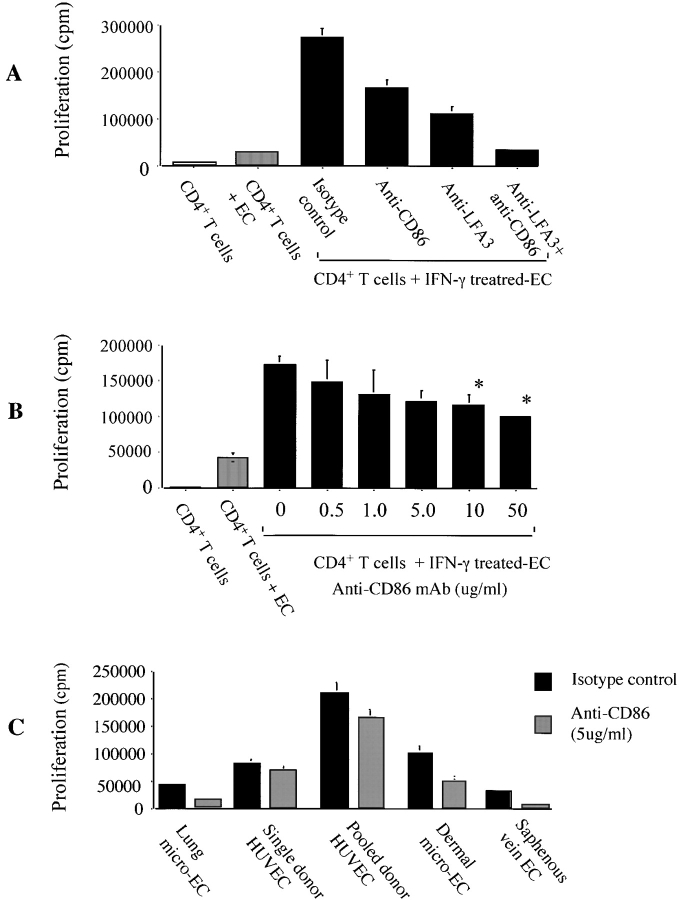
Figure 2.
Function of CD80 and CD86 in allogeneic CD4+ T cell–EC cocultures. CD4+ T cells were cultured alone (white bars), with untreated HUVECs (gray bars), or with HUVECs that were treated with IFN-γ (1,000 U/ml) for 72 h (black bars). (A) Anti-CD86 antibody (IT2.2, clone, 10 μg/ml), LFA-3 (5 μg/ml), or combinations were added into cocultures of CD4+ T cells with IFN-γ–treated HUVECs as indicated. Data represents the mean of 10 experiments performed in triplicate cultures ± 1 SD. (B) Dose–response effect of anti-CD86 antibody (IT2.2 clone) on CD4+ T cell alloproliferation. We also find that anti-CD86 mAbs inhibit EC-induced CD4+ T cell IL-2 production (data not shown). Results are representative of four similar experiments performed in triplicate cultures ± 1 SD. (C) Coculture of CD4+ T cells with various IFN-γ–treated microvascular endothelial cells in the absence (black bars) or presence (gray bars) of anti-CD86 mAbs (10 μg/ml, IT2.2 clone). Results are representative of two similar experiments performed in triplicate cultures ± 1 SD (*P < 0.05). (A–C) In all experiments, proliferation was assessed after 6 d of coculture by [3H]thymidine uptake.