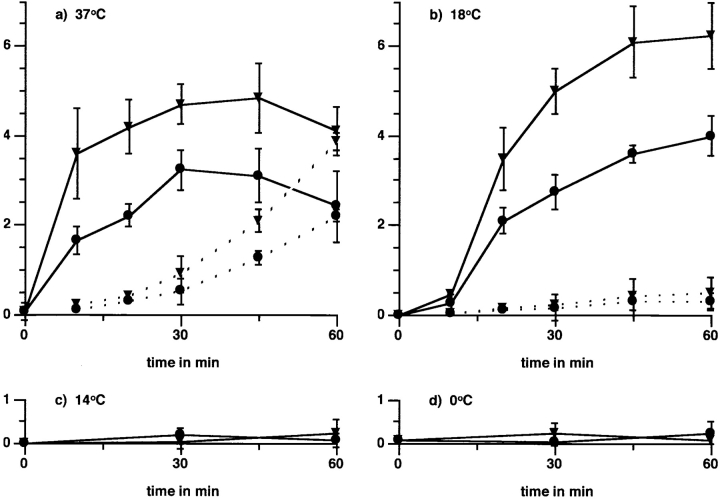
Figure 7.
Temperature sensitivity of apoptotic cell or OS binding and internalization by macrophages. Particle binding by macrophages, which use both αvβ3 and αvβ5, retains the fast macrophage binding kinetics and onset of binding. J774 cells were challenged with apoptotic cells or OS after 20 min preincubation with PMA (▾) or solvent alone (•) and preequilibration to different temperatures for 20 min. To establish binding indices for all temperatures, internalized particle counts were subtracted from counts representing bound plus internalized particles. Binding indices are plotted in solid lines for four temperatures: (a) incubation at 37°C, (b) 18°C, (c) 14°C, and on ice (at 0°C) (d). At both 37°C and 18°C, binding by PMA-treated cells exceeded that by control cells by approximately the same margin at all times. Thus, the onset of αvβ5-mediated binding by macrophages was fast and there was no lag phase as characteristic for αvβ5 binding by RPE. Reequilibration of cells to permissive temperatures after 60 min on ice restored their binding activity, and led to increased binding in the presence of PMA (data not shown), excluding nonspecific cell damage. Internalization indices are plotted in dotted lines. Internalization occurred regardless of treatment at 37°C (a). Cells at 18°C bound but did not internalize particles (b), but internalized prebound particles within 45 min after being shifted to 37°C (data not shown). Complement-opsonized zymosan binding occurred efficiently at all temperatures (data not shown). Values shown represent means ± SEM (n = 3) of results obtained with OS. Identical results were obtained challenging macrophages with apoptotic cells.