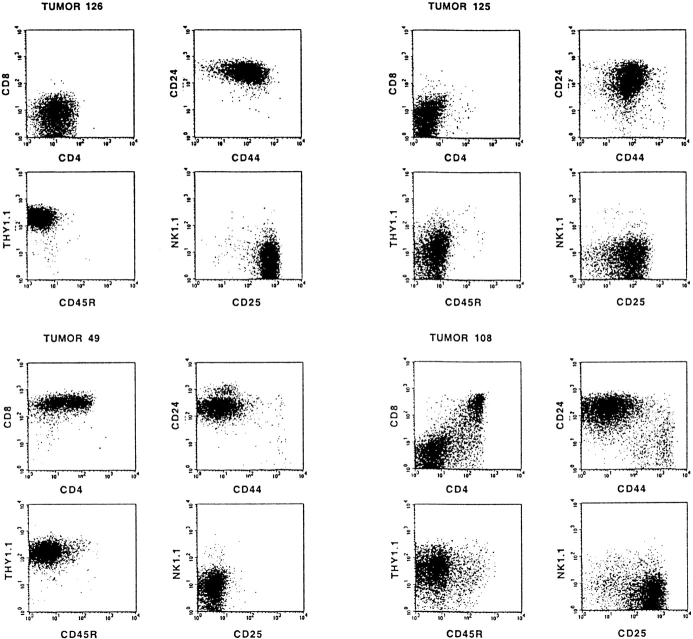
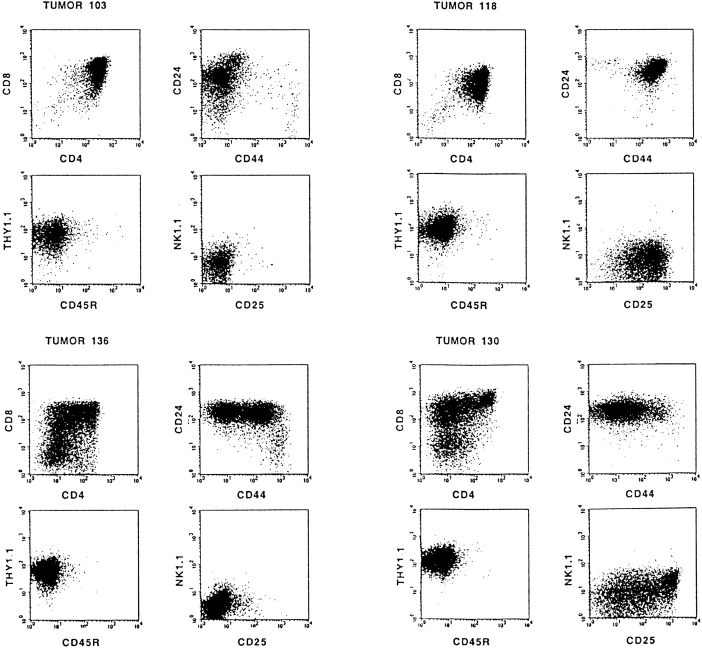
Figure 2.
Most T cell tumors in MoMuLV-infected Rag2-deficient mice bypass the Rag2-mediated differentiation arrest. Typical examples of FACS™ analysis of MoMuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in Rag2-deficient mice are shown. In Rag-deficient mice, differentiation of thymocytes is arrested at the CD4−8−24+25+44low DN stage of α/β T cell development. Whereas tumors 125 and 126 are representative examples for DN tumors, most lymphomas bypass this differentiation arrest and develop into DP or combined DN/DP immature T cell lymphomas. For example, tumor 49 represents a “transitional tumor” from the ISP to DP stage, tumor 108 is a DN/DP tumor, tumors 103 and 118 are DP, and tumors 130 and 136 are “differentiating tumors” from DN to ISP to DP. The tumors with a mixed phenotype, like 49, 130, and 136, are clonal, as the genomes of sorted fractions carry identical proviral insertions (data not shown).