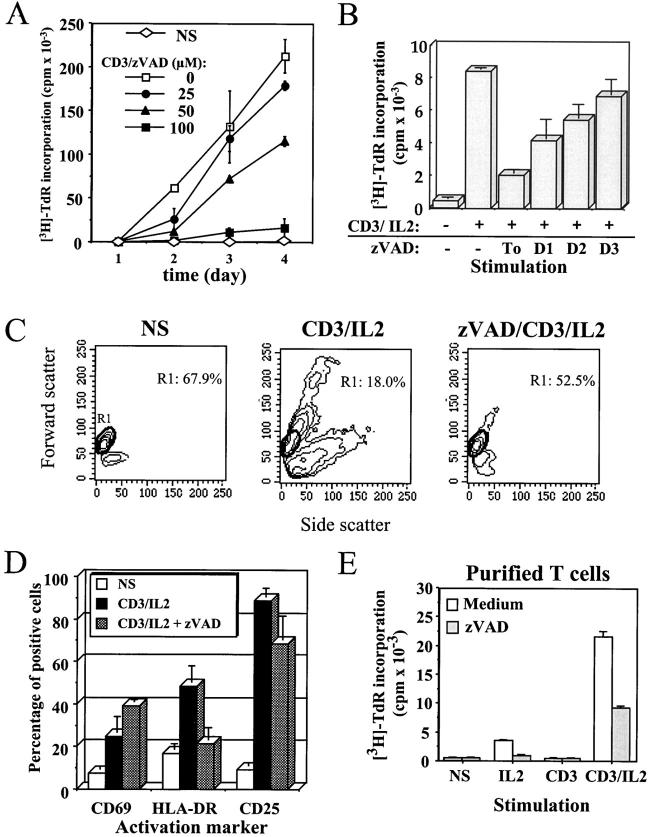
Figure 1.
The general caspase inhibitor zVAD blocks anti-CD3–induced T cell activation. (A) Inhibition of PBMC proliferation by zVAD. Purified PBMCs were cultured in medium alone (NS) or stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 and 20 U/ml IL-2 (CD3) in the presence of the indicated concentration of zVAD. At each time point, 1 μCi/well of [3H]thymidine was added for the last 6 h of culture, cells were harvested, and incorporated thymidine was counted by liquid scintillation. [3H]Thymidine ([3H]-TdR) incorporation is expressed as mean cpm ± SEM of triplicate cultures. Results are representative of three experiments where full kinetics was carried out. (B) zVAD does not inhibit cell cycle machinery. Fresh PBMCs were placed in RPMI medium, and 100 μM of zVAD was added 1 h before or 1, 2, or 3 d after stimulation in the presence of anti-CD3 antibody and IL-2. Cells were cultured for 4 d at 37°C, and [3H]thymidine was added for the last 6 h of incubation. Thymidine incorporation at day 4 is expressed as cpm ± SEM from triplicate cultures. Two independent experiments gave similar results. (C) Inhibition of blastic transformation by zVAD. Change in PBMCs morphology was monitored by flow cytometric analysis of cellular forward (y-axis) and side (x-axis) scatter. Percentage of resting PBMCs (region R1) is indicated inside dot plots. One representative experiment out of five is shown. (D) zVAD affects the expression of MHC class II. Surface staining was performed for CD69, HLA-DR, and CD25 on PBMCs activated for 4 d with anti-CD3/IL-2, in the presence or absence of 100 μM of zVAD. One representative experiment of three is shown. (E) The effect of zVAD is independent of accessory cells. Purified T lymphocytes isolated from PBMCs by negative selection were preincubated for 1 h in medium alone or with 100 μM zVAD, and cultured for 4 d without stimulation (NS) or in the presence of IL-2, anti-CD3, or both. Proliferation was assessed by [3H]thymidine incorporation as described in A. Results are representative of two independent experiments.